Harrisonia abyssinica Oliv. - Journal of Chemical and ...
Harrisonia abyssinica Oliv. - Journal of Chemical and ...
Harrisonia abyssinica Oliv. - Journal of Chemical and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Mubo A. Sonibare et al J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2012, 4(1):800-807<br />
_____________________________________________________________________________________<br />
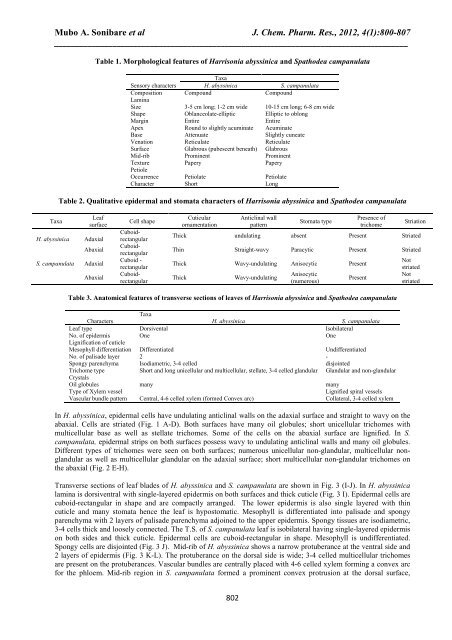
Taxa<br />
H. <strong>abyssinica</strong><br />
Table 1. Morphological features <strong>of</strong> <strong>Harrisonia</strong> <strong>abyssinica</strong> <strong>and</strong> Spathodea campanulata<br />
Taxa<br />
Sensory characters H. <strong>abyssinica</strong> S. campanulata<br />
Composition Compound Compound<br />
Lamina<br />
Size 3-5 cm long; 1-2 cm wide 10-15 cm long; 6-8 cm wide<br />
Shape Oblanceolate-elliptic Elliptic to oblong<br />
Margin Entire Entire<br />
Apex Round to slightly acuminate Acuminate<br />
Base Attenuate Slightly cuneate<br />
Venation Reticulate Reticulate<br />
Surface Glabrous (pubescent beneath) Glabrous<br />
Mid-rib Prominent Prominent<br />
Texture Papery Papery<br />
Petiole<br />
Occurrence Petiolate Petiolate<br />
Character Short Long<br />
Table 2. Qualitative epidermal <strong>and</strong> stomata characters <strong>of</strong> <strong>Harrisonia</strong> <strong>abyssinica</strong> <strong>and</strong> Spathodea campanulata<br />
Leaf<br />
surface<br />
Adaxial<br />
Abaxial<br />
S. campanulata Adaxial<br />
Abaxial<br />
Cell shape<br />
CuboidrectangularCuboidrectangular<br />
Cuboid -<br />
rectangular<br />
Cuboidrectangular<br />
Cuticular<br />
ornamentation<br />
802<br />
Anticlinal wall<br />
pattern<br />
Stomata type<br />
Presence <strong>of</strong><br />
trichome<br />
Striation<br />
Thick undulating absent Present Striated<br />
Thin Straight-wavy Paracytic Present Striated<br />
Thick Wavy-undulating Anisocytic Present<br />
Thick Wavy-undulating<br />
Anisocytic<br />
(numerous)<br />
Present<br />
Table 3. Anatomical features <strong>of</strong> transverse sections <strong>of</strong> leaves <strong>of</strong> <strong>Harrisonia</strong> <strong>abyssinica</strong> <strong>and</strong> Spathodea campanulata<br />
Taxa<br />
Characters<br />
H. <strong>abyssinica</strong><br />
S. campanulata<br />
Leaf type Dorsivental Isobilateral<br />
No. <strong>of</strong> epidermis<br />
Lignification <strong>of</strong> cuticle<br />
One One<br />
Mesophyll differentiation Differentiated Undifferentiated<br />
No. <strong>of</strong> palisade layer 2 -<br />
Spongy parenchyma Isodiametric, 3-4 celled disjointed<br />
Trichome type<br />
Crystals<br />
Short <strong>and</strong> long unicellular <strong>and</strong> multicellular, stellate, 3-4 celled gl<strong>and</strong>ular Gl<strong>and</strong>ular <strong>and</strong> non-gl<strong>and</strong>ular<br />
Oil globules many many<br />
Type <strong>of</strong> Xylem vessel Lignified spiral vessels<br />
Vascular bundle pattern Central, 4-6 celled xylem (formed Convex arc) Collateral, 3-4 celled xylem<br />
In H. <strong>abyssinica</strong>, epidermal cells have undulating anticlinal walls on the adaxial surface <strong>and</strong> straight to wavy on the<br />
abaxial. Cells are striated (Fig. 1 A-D). Both surfaces have many oil globules; short unicellular trichomes with<br />
multicellular base as well as stellate trichomes. Some <strong>of</strong> the cells on the abaxial surface are lignified. In S.<br />
campanulata, epidermal strips on both surfaces possess wavy to undulating anticlinal walls <strong>and</strong> many oil globules.<br />
Different types <strong>of</strong> trichomes were seen on both surfaces; numerous unicellular non-gl<strong>and</strong>ular, multicellular nongl<strong>and</strong>ular<br />
as well as multicellular gl<strong>and</strong>ular on the adaxial surface; short multicellular non-gl<strong>and</strong>ular trichomes on<br />
the abaxial (Fig. 2 E-H).<br />
Transverse sections <strong>of</strong> leaf blades <strong>of</strong> H. <strong>abyssinica</strong> <strong>and</strong> S. campanulata are shown in Fig. 3 (I-J). In H. <strong>abyssinica</strong><br />
lamina is dorsiventral with single-layered epidermis on both surfaces <strong>and</strong> thick cuticle (Fig. 3 I). Epidermal cells are<br />
cuboid-rectangular in shape <strong>and</strong> are compactly arranged. The lower epidermis is also single layered with thin<br />
cuticle <strong>and</strong> many stomata hence the leaf is hypostomatic. Mesophyll is differentiated into palisade <strong>and</strong> spongy<br />
parenchyma with 2 layers <strong>of</strong> palisade parenchyma adjoined to the upper epidermis. Spongy tissues are isodiametric,<br />
3-4 cells thick <strong>and</strong> loosely connected. The T.S. <strong>of</strong> S. campanulata leaf is isobilateral having single-layered epidermis<br />
on both sides <strong>and</strong> thick cuticle. Epidermal cells are cuboid-rectangular in shape. Mesophyll is undifferentiated.<br />
Spongy cells are disjointed (Fig. 3 J). Mid-rib <strong>of</strong> H. <strong>abyssinica</strong> shows a narrow protuberance at the ventral side <strong>and</strong><br />
2 layers <strong>of</strong> epidermis (Fig. 3 K-L). The protuberance on the dorsal side is wide; 3-4 celled multicellular trichomes<br />
are present on the protuberances. Vascular bundles are centrally placed with 4-6 celled xylem forming a convex arc<br />
for the phloem. Mid-rib region in S. campanulata formed a prominent convex protrusion at the dorsal surface,<br />
Not<br />
striated<br />
Not<br />
striated