Abstract
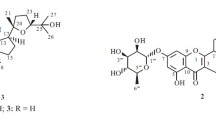
Chemical examinations of Cleistanthus collinus Roxb., a poisonous tree from India, and Cleistanthus patulus Muell. Arg. have resulted in isolation of a number of arylnaphthalide lignans and their glycosides as well as some furofuranoid lignans. While Cleistanthus gracilis Hook. f. from Thailand afforded an unusual glucoside of 2-β-hydroxy-8-azabicyclo-(5,0,2)-4β, 9β-epoxynona-5,7-diene, C. schlechteri from South Africa was the first reported source of the pimarane diterpenes. Cleistanthin A and cleistanthin B, diphyllin glycosides isolated from C. collinus were reported to exhibit cytotoxicity on several cancer cell lines. Cleistanthin A was found to cause DNA strand breaks and induce apoptosis in cultured cells while cleistanthin B caused G1 arrest and induced apoptosis in mammalian cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjaneyulu ASR, Ramaiah PR, Row LR (1975a) The structure of wodeshiol—the first of a new series of lignans. Tetrahedron Lett 34:2961–2964
Anjaneyulu ASR, Ramaiah PR, Row LR (1975b) A new diphyllin glycoside from Cleistanthus collinus. Phytochemistry 14:1875–1876
Anjaneyulu ASR, Ramaiah PR, Row LR (1977) Crystalline constituents of Euphorbiaceae: Part XVI—a new diphyllin glycoside from Cleistanthus collinus Roxb. Indian J Chem Section B:10–11
Anjaneyulu ASR, Ramaiah PR, Row LR, Venkateswarlu R, Pelter A, Ward RS (1981) New lignan from the heartwood of Cleistanthus collinus. Tetrahedron 37:3641–3652
Candy HA, Pakshong JM, Pegel KH (1970) Pimarane diterpenes from Cleistanthus schlechteri. J Chem Soc (C):2536–2538
Govindachari TR, Sathe SS, Viswanathan N, Pai BR, Srinivasan M (1969) Chemical constituents of Cleistanthus collinus (Roxb.). Tetrahedron 25:2815–2821
Kumar CPP, Pande G, Shanmugam G (1998) Cleistanthin B causes G1 arrest and induces apoptosis in mammalian cells. Apoptosis 3:413–419
Lakshmi TG, Srimannaryana G, Subbarao HV (1970) Diphyllin O-glycoside from Cleistanthus collinus bark. Curr Sci 39:395
Meenakshi J, Shanmugam G (2000a) Cleistanthin A, a diphyllin glycoside from Cleistanthus collinus, is cytotoxic to PHA-stimulated (proliferating) human lymphocytes. Drug Dev Res 51:187–190
Meenakshi J, Shanmugam G (2000b) Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity by cleistanthin A, a diphyllin glycoside from Cleistanthus collinus. Drug Dev Res 50:193–194
McGarry EJ, Pegel KH, Phillips L, Waight ES (1969) Cleistanthol, a novel diterpene from Cleistanthus schlechteri (Euphorbiaceae). Chem Comm 1074
McGarry EJ, Pegel KH, Phillips L, Waight ES (1971) The constitution of the aromatic Diterpene cleistanthol. J Chem Soc (C):904–909
Pinho P, Naengchomnong W, Kijjoa A, Nazareth N, Silva AMS, Eaton G, Herz W (2006) An unusual glucoside from Cleistanthus gracilis. Phytochemistry 67:1789–1792
Prabhakaran C, Kumar P, Panneerselvam N, Rajesh S, Shanmugam G (1996) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of cleistanthin B in normal and tumour cells. Mutagenesis 11:553–557
Pradheepkumar CP, Shanmugam G (1999) Anticancer potential of cleistanthin A isolated from the tropical plant Cleistanthus collinus. Oncol Res 11:225–232
Pradheepkumar CP, Pannerselvam N, Shanmugam G (2000) Cleistanthin A causes DNA strand breaks and induces apoptosis in cultured cells. Mutation Res/Genet Toxicol Environ Mutat 464:185–193
Ramesh C, Ravindranath N, Ram TS, Das B (2003) Arylnaphthalide lignans from Cleistanthus collinus. Chem Pharm Bull 51:1299–1300
Sastry KV, Rao V (1983) Isolation and structure elucidation of cleistanthoside A. Planta Med 47:227–229
Sastry KV, Rao EV, Buchanan JG, Sturgeon RJ (1987) Cleistanthoside B, a diphyllin glycoside from Cleistanthus patulus heartwood. Phytochemistry 26:1153–1154
Satayanarayana P, Subrahmanyam P, Rao K (1984) Chemical constituents of Cleistanthus collinus roots. Indian J Pharm Sci 46:95–96
Acknowledgements
We thank Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) and CIIMAR (Programa Plurianual) for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinho, P.M.M., Kijjoa, A. Chemical constituents of the plants of the genus Cleistanthus and their biological activity. Phytochem Rev 6, 175–182 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-006-9027-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-006-9027-z