Abstract
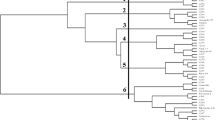
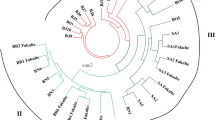
A comparison of the efficiency of RAPD and ISSR primers using different genetic parameters like polymorphism percentage, effective alleles per locus (Aep), genetic diversity per locus (Hep), Shannon diversity index (I), polymorphic information content (PIC) and marker index (MI) has been performed in 8 Indian grown Corchorus spp. (2n = 14) of the family Tiliaceae (C. capsularis L., C. olitorius L., C. aestuans L., C. fascicularis Lamk., C. pseudocapsularis L., C. pseudoolitorius I. and Z., C. tridens L. and C. trilocularis L.). The objective of the work is to develop a simple, efficient and cost effective primer based system for quick genetic evaluation of Corchorus germplasms. Result indicated that OPA 03, OPA 05, OPA 06, OPB 03, OPB 06, OPC 05 and OPC 10 among the employed RAPD markers and (GA)12, (CA)8GC and (GATA)4 among ISSR primers are efficient and effective. Further, relatedness between the species has also been noted using principal component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis by Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic Mean (UPGMA) with an objective for efficient breeding and crop improvement. Unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed from molecular data of the studied species revealed possible divaricated mode of origin of Corchorus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME. Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome. 1993;36:181–6.
Basu A, Ghosh M, Mayer R, Powel W, Basak SL, Sen SK. Analysis of genetic diversity in cultivated jute determined by means of SSR markers and AFLP profiling. Crop Sci. 2004;44:678–85.
Datta RM, Panda BS, Roy K, Bose MM, De TK. Cytotaxonomic studies of different Corchorus (jute) species. Bot Mag (Tokyo). 1966;79:467–73.
Datta RM, Mukhopadhaya D, Panda BS, Sasmal PK. Cytotaxonomic studies of different Corchorus (jute) species II. Cytologia. 1975;40:685–92.
Dillon WR, Goldstein M. Multivariate analysis methods and application. New York: Wiley; 1984.
Garcia-Vallve S, Palau J, Romeu A. Horizontal gene transfer in glycosyl hydrolases inferred from codon usage in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Mol Biol Evol. 1999;9:1125–34.
Godwin ID, Aitken E, Smith LW. Application of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers to plant genetics. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:1524–8.
Gupta MY, Chyi SJ, Romero-Severson J, Owen JL. Amplification of DNA markers from evolutionarily diverse genomes using single primers of simple sequence repeat. Theor Appl Genet. 1994;89:998–1006.
Hossain MD, Haque S, Khan H. DNA fingerprinting of jute germplasm by RAPD. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;35:414–9.
Hossain MB, Awal A, Rahman MA, Haque S, Khan H. Distinction between cold-sensitive and -tolerant jute by DNA polymorphisms. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;36:427–32.
Huq S, Islam MS, Sajib AA, Ashraf N, Haque S, Khan H. Genetic diversity and relationships in jute (corchorus spp.) revealed by SSR markers. Bangladesh J Bot. 2009;38:153–61.
Islam AS, Rashid A. First successful hybridization between the two jute yielding species, Corchorus olitorius (Tossa) X C. capsularis (White). Nature. 1960;185:258–9.
Jain JP. Statistical techniques in quantitative genetics. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd.; 1982.
Karmakar PG, Hazra SK, Ramasubramanian T, Mandal RK, Sinha MK, Sen HS, editors. Jute and allied fibre updates: production and technology. Brrackpore: CRIJAF; 2008.
Kesari V, Sathyanarayana VM, Parida A, Rangan L. Molecular marker-based characterization in candidate plus trees of Pongamia pinnata, a potential biodiesel legume. AoB Plants Vol. 2010, plq017, doi: 10.1093/aobpla/plq017
Khatun A. Recent agricultural developments in jute, kenaf and mesta through traditional and biotechnological approaches. A seminar on jute and kenaf held in Myanmar organized by the Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation, Myanmar Jute Industries and the International Jute Study Group (IJSG). Myanmar; 2007. p. 1–13.
Kundu BC. Origin of jute. Indian J Genet. 1951;11:95–9.
Lacerda DR, Acedo MDP, Lemos Filho JP, Lovato MB. Genetic diversity and structure of natural populations of Plathymenia reticulata (Mimosoideae), a tropical tree from the Brazilian Cerrado. Mol Ecol. 2001;10:1143–52.
Mahapatra AK, Saha A, Basak SL. Origin, taxonomy and distribution of Corchorus species in India. Green J. 1998;1:64–82.
Mahapatra AK, Saha A. Genetic resources of jute and allied fibre crops. In: Karmakar PG, Hazra SK, Ramasubramanian T, Sinha MK, Sen HS, editors. Jute and allied fibres updates: production and technology. Brrackpore: CRIJAF; 2008. p. 18–37.
Maity S, Datta AK. Cytomorphological studies in F1 hybrids (Corchorus capsularis L. × Corchorus trilocularis L.) of jute (Tiliaceae). Comp Cytogenet. 2008;2:143–9.
Maity S, Datta AK. Karyomorphology in nine species of jute (Corchorus L., Tiliaceae). Cytologia. 2009;74:273–9.
Maity S, Datta AK. Cytomorphological studies in F2, F3 and induced amphidiploid of jute (Corchorus trilocularis L. X Corchorus capsularis L.). Nucleus. 2010;53:85–7.
Mandal A, Datta AK. Secondary chromosome associations and cytomixis in Corchorus spp. Cytologia. 2011;76:337–43.
Mandal A, Datta AK. Inter- and intra-plant variations in cytomictic behavior of chromosomes in Corchorus fascicularis Lamk. (Tiliaceae). Cytologia. 2012;77:269–77.
Martynov SP, Dobrotvorskaya TV, Dotlacil L, Stehno Z, Faberova I, Bares I. Genealogical approach to the formation of the winter wheat core collection. Russian J Genet. 2003;39:917–23.
Mir RR, Rustagi S, Sharma S, Singh R, Goyal A, Kumar J, et al. A preliminary genetic analysis of fibre traits and the use of new genomic SSRs for genetic diversity in jute. Euphytica. 2008;161:413–27.
Muthusamy S, Kanagarajan S, Ponnusamy S. Efficiency of RAPD and ISSR markers system in accessing genetic variation of rice bean (Vigna umbellata) landraces. Electron J Biotechn. 2008;11. doi: 10.2225/vol11-issue3-fulltext-8
Noormohammadi Z, Fasihee A, Homaee-Rashidpoor S, Sheidai M, Baraki SG, Mazooji A, et al. Genetic variation among Iranian pomegranates (Punica granatum L.) using RAPD, ISSR and SSR markers. Australian J Crop Sci. 2012;6:268–75.
Ogunkanmi LA, Okunowo WO, Oyelakin OO, Oboh BO, Adesina OO, Adekoya KO, et al. Assessment of genetic relationships between two species of jute plants using phenotypic and RAPD markers. Int J Bot. 2010;6:107–11.
Palve SM, Sinha MK, Chattopadhyay S. Genetic variability for fibre strength and fineness in wild relative of genus Corchorus. In: Hazra SK, Karmakar PG, editors. Proceedings of National Seminar on Diversified Uses of Jute and Allied Fibre Crops. CRIJAF, NIRJAFT and IFS(ER), Barrackpore, India; 2004. p. 99–103.
Parsons JB, Newbury HT, Jackson MT, Ford-Lloyd BV. Contrasting genetic diversity relationships are revealed in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using different marker types. Mol Breed. 1997;3:115–25.
Patamsytė J, Čėsnienė T, Naugžemys D, Kleizaitė V, Vaitkūnienė, Rančelis V, et al. Genetic diversity of warty cabbage (Bunias orientalis L.) revealed by RAPD and ISSR markers. Žemdirbystė Agric. 2011;98:293–300.
Patel GI, Datta RM. Pollen grain studies in various types of Corchorus olitorius L, C capsularis and some other species of Corchorus. Grana. 1958;1:18–24.
Patzak J. Comparison of RAPD, STS, ISSR and AFLP molecular methods used for assessment of genetic diversity in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica. 2001;121:9–18.
Purseglove JW. Tropical crops: dicotyledons 2. Longmans: Green; 1968.
Qi J, Zhou D, Wu W, Lin L, Wu J, Fang P. Application of ISSR technology in genetic diversity detection of jute. Chin J Appl Ecol. 2003;14:1473–7.
Qian W, Ge S, Hong DY. Genetic variation within and among populations of wild rice Oryza granulata from China detected by rRAPD and ISSR markers. Theor Appl Genet. 2001;102:440–9.
Roy A, Bandyopadhyay A, Mahapatra AK, Ghosh SK, Singh NK, Bansal KC, et al. Evaluation of genetic diversity in jute (Corchorus) species using STMS, ISSR and RAPD markers. Plant Breed. 2006;125:292–7.
Saini M, Singh S, Hussain Z, Sikka VK. RAPD analysis in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek.] II: a comparison of efficiency parameters of RAPD primer. Indian J Biotech. 2010;9:137–46.
Tao AF, Qi JM, Li ML, Fang PP, Lin LH, Xu JT. Origin and evolution of jute analyzed by SRAP and ISSR methods. Chin J Agric Sci. 2012;45:16–25.
Weir BS. Genetic data analysis II: methods for discrete population genetic data. Sunderland: Sinauer Publishers; 1996.
Yu LX, Nguyen NT. Genetic variation detected with RAPD markers among upland and lowland rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet. 1994;87:668–72.
Zhou Y, Zhou C, Yao H, Liu Y, Tu R. Application of ISSR markers in detection of genetic variation among Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb) cultivars. Life Sci J. 2008;5:6–12.
Acknowledgment
The aided research grant by University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, A., Datta, A.K., Datta, S. et al. Genetic assessment of eight Corchorus spp. (Tiliaceae) using RAPD and ISSR markers. Nucleus 56, 23–30 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-013-0076-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-013-0076-6