Abstract
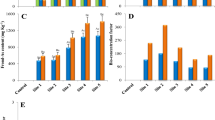
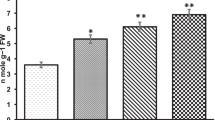
The arsenic (As) contamination demands its remediation from the environment which is naturally possible by the application of Pteris vittata L. However, biomonitoring of phytoremediation potential of P. vittata at chromosomal and DNA level is still meager. The present study was designed to biomonitor the phytoremediation efficiency of P. vittata through phytotoxic and cyto-genotoxic biomarkers assessment using Trigonella foenum-graecum L. (Fenugreek; Methi) as test system. Study revealed hyperaccumulation potential of P. vittata which extracted arsenic in its tissues. Biomonitoring evaluation depicted that phytotoxic damage was reduced in Trigonella exposed to remediated soil, which was revealed through reduced electrolyte leakage, hydrogen peroxide and MDA content. Moreover, cyto-genetic endpoints like mitotic depression (44.03%), relative abnormality rate (16.6%) and chromosomal abnormality frequency (1.06%) were also lesser in test plants grown in remediated soil compared to those grown in non-remediated soil. Along with this various chromosomal aberrations like stickiness, breaks, laggards, bridges, fragmentations and micronuclei were also augmented in test plants exposed to non-remediated arsenic enriched soil. It was evident that arsenic enriched soil caused toxicity to plants in dose-dependent manner that was assessable through the analysis of biochemical parameters and cyto-genetic biomarkers. The cyto-genetic biomarkers are very efficient, simple and non-expensive tools to biomonitor arsenic toxicity at chromosomal as well as DNA level to assess the remediation potential of P. vittata in field conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaal KA, EL-Maghraby LM, Elansary H, Hafez YM, Ibrahim EI, El-Banna M, El-Esawi M, Elkelish A, (2020) Treatment of sweet pepper with stress tolerance-inducing compounds alleviates salinity stress oxidative damage by mediating the physio-biochemical activities and antioxidant systems. Agronomy 10(1):26
Abdelaal KA, MazrouYS HYM (2020) Silicon foliar application mitigates salt stress in sweet pepper plants by enhancing water status, photosynthesis, antioxidant enzyme activity and fruit yield. Plants 9(6):733
Abdul-Baki AA, Anderson JD (1973) Vigour determination in soybean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Sci 13:630–632
Abu-Muriefah SS (2015) Effects of Silicon on membrane characteristics, photosynthetic pigments, antioxidative ability, and mineral element contents of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants grown under Cd and Pb stress. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci 2(6):1–17
AL-Kahtani MD, Attia KA, Hafez YM, Khan N, Eid AM, Ali MA, Abdelaal KA (2020) Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and antioxidant defense system can display salt tolerance of salt acclimated sweet pepper plants treated with chitosan and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Agronomy 10(8):1180
Amin A, Alkaabi A, Al-Falasi S, Daoud SA (2005) Chemo preventive activities of Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) against breast cancer. Cell Bio Int 29(8):687–694
AOSA (1990) Rules for testing seeds, USA. Seed Tech 12:1–112
Atsdr U (2007) Toxicological profile for arsenic. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Division of Toxicology, Atlanta, GA.
Bhat TM, Sana C, Ansari MYK, Rumana A (2012) Genotoxicity and molecular screening of proteins in root tip cells of Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek var-Azad) under cadmium stress condition. Int J Plant Physiol Biochem 4(3):46–51
Bhattacharya AK, Lodh R (2018) Arsenic contamination in the groundwater of India with a special focus on the stabilization of arsenic laden sludge from arsenic filters. Elect J Geotech Eng 23:575–600
Bianchi J, Fernandes TCC, Marin-Morales MA (2016) Induction of mitotic and chromosomal abnormalities on Allium cepa cells by pesticides imidacloprid and sulfentrazone and the mixture of them. Chemosphere 144:475–483
Cabrera GL, Rodriguez DMG (1999) Genotoxicity of soil from farmland irrigated with wastewater using three plant bioassays. Mutat Res/fund Mol Mech Mut 426(2):211–214
Cokkizgin A, Cokkizgin H (2010) Effects of lead (PbCl2) stress on germination of lentil (Lens culinaris Medic.) lines. Afr J Biotech 9(50):8608–8612
de Souza RB, de Souza CP, Bueno OC, Fontanetti CS (2017) Genotoxicity evaluation of two metallic-insecticides using Allium cepa and Tradescantia pallida: a new alternative against leaf-cutting ants. Chemosphere 168:1093–1099
Devi SR, Prasad MNV (1998) Copper toxicity in Ceratophyllum demersum L. (Coontail), a free floating macrophyte: response of antioxidant enzymes and antioxidants. Plant Sci 138:157–165
Dong YS, Wang JL, Feng DY, Qin HZ, Wen H, Yin ZM, Gao GD, Li C (2014) Protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress and brain edema in an experimental rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Int J Med Sci 11(3):282
Dwivedi S, Tripathi RD, Srivastava S, Singh R, Kumar A, Tripathi P, Dave R, Rai UN, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Tuli R, Adhikari B, Bag MK (2010) Arsenic affects mineral nutrients in grains of various Indian rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes grown under arsenic-contaminated soils of West Bengal. Protoplasma 245:113–124
Elleuch A, Chaâbene Z, Grubb DC, Drira N, Mejdoub H, Khemakhem B (2013) Morphological and biochemical behavior of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) under copper stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:46–53
Farooq MA, Islam F, Ali B, Najeeb U, Mao B, Gill RA, Yan G, Siddique KHM, Zhou W (2016) Arsenic toxicity in plants: cellular and molecular mechanisms of its transport and metabolism. Environ Exp Bot 132:42–52
Fatma F, Verma S, Kamal A, Srivastava A (2018) Monitoring of morphotoxic, cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of mancozeb using Allium assay. Chemosphere 195:864–870
Firbas P, Amon T (2014) Chromosome damage studies in the onion plant Allium cepa L. Caryologia 67:25–35
Fiskesjö G (1985) The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 102(1):99–112
Gonzaga MI, Santos JA, Ma LQ (2008) Phytoextraction by arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. from six arsenic-contaminated soils: repeated harvests and arsenic redistribution. Environ Pollut 154(2):212–218
Gupta K (2014) Biomonitoring of lead (Pb) toxicity through aquatic Macrophyte Eichhornia crassipes. Int J Environ 3(2):12–19
Gupta K, Gaumat S, Mishra K (2011) Oxidative stress: a biological technique for the assay of chromium induced phytotoxicity. Pollut Res 30(4):557–564
Gupta K, Gaumat S, Mishra K (2012) Studies on phyto-genotoxic assessment of tannery effluent on Allium cepa. J Environ Biol 33:557–563
Gupta K, Mishra K, Srivastava S, Kumar A (2018) Cytotoxic assessment of chromium and arsenic using chromosomal behavior of root meristem in Allium cepa L. Bull Environ Cont Toxicol 100:803–808
Gupta K, Srivastava A, Kumar A (2020a) Arsenic: threat to water as well as soil. Contaminants and clean technologies. Tylor Francis Group 10:166–187
Gupta K, Srivastava A, Srivastava S, Kumar A (2020b) Phyto-genotoxicity of arsenic contaminated soil from Lakhimpur-Kheri, India on Vicia faba L. Chemosphere 241:125063
Gupta K, Srivastava S, Saxena G, Kumar A (2021) Evaluation of phytoremediation potential of Pteris vittata L. on arsenic contaminated soil using Allium cepa bioassay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03291-8
Han YH, Jia MR, Wang SS, Deng JC, Shi XX, Chen DL, Chen Y, Ma LQ (2020) Arsenic accumulation and distribution in Pteris vittata fronds of different maturity: Impacts of soil As concentrations. Sci Tot Environ 715:135298
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198
Hu Y, Li J, Lou B, Wu R, Wang G, Lu C, Wang H, Pi J, Xu Y (2020) The role of reactive oxygen species in arsenic toxicity. Biomolecules 10(2):240
Kirsch VM, Plas G, Elhajouji A, Lukamowicz M, Gonzalez L, VandeLoock K (2011) The in vitro MN assay in 2011: origin and fate, biological significance, protocols, high throughput methodologies and toxicological relevance. Arch Toxicol 85(8):873–899
Kumar A, Ansari MI, Srivastava S, Saxena G, Gupta K (2020b) Genetic engineering to reduce toxicity and increase accumulation of toxic metals in plants. In: Sustainable solutions for elemental deficiency and excess in crop plants, 978-981-15-8635-4, 490120_1_En. Springer Nature
Kumar A, Dixit G, Singh AP, Srivastava S, Mishra K, Tripathi RD (2016) Selenate mitigates arsenite toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by reducing arsenic uptake and ameliorates amino acid content and thiol metabolism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:350–359
Kumar A, Singh PK, Srivastava S, Dwivedi S, Tripathi RD, Awasthi G, Gupta K, Ansari MI (2020b) A comparative study on effect of arsenic on thiolic ligands and phytochelatins in contrasting arsenic accumulating rice genotypes. Int J Plant Environ 6(02):110–117
Kumar A, Singh RP, Singh PK, Awasthi S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Tripathi RD (2014a) Selenium ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress through modulation of antioxidant enzymes and thiols in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol 23:1153–1163
Kumar A, Tripathi RD, Singh RP, Dwivedi S, Chakrabarty D, Mallick S, Trivedi PK, Adhikari B (2014b) Evaluation of amino acid profile in contrasting arsenic accumulating rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes under arsenic stress grown in hydroponic condition. Biol Plant 58(4):733–742
Kumar G, Srivastava N (2011) Genotoxic effects of two commonly used food additives of boric acid and sunset yellow in root meristems of Trigonella foenum-graecum. J Environ Health Sci Eng 8(4):361–366
Kumar N, Mallick S, Yadava RN, Singh AP, Sinha S (2013) Co-application of selenite and phosphate reduces arsenite uptake in hydroponically grown rice seedlings: toxicity and defense mechanism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 91:171–179
Lessl JT, Luo J, Ma LQ (2014) Pteris vittata continuously removed arsenic from non-labile fraction in three contaminated-soils during 3.5-year of phytoextraction. J Hazard Mater 279:485–492
Liao XY, Chen TB, Xie H, Xiao XY (2004) Effect of application of P fertilizer on efficiency of As removal in contaminated soil using phytoremediation: field demonstration. Acta Sci Circum 24:455–462
Ma LQ, Komar KM, Tu C, Zhang W, Cai Y, Kennelley ED (2001) A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic. Nature 409(6820):579–579
Majewska AE, Wolska E, Sliwinska M, Furmanowa N, Urbanska A, Pietrosiuk A, Zobel A, Kuran M (2003) Antimitotic effect, G2/M accumulation, chromosomal and ultrastructure changes in meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. root tips treated with the extract from Rhadiolarosea roots. Caryology 56:337–351
Menon P, Joshi N, Joshi A (2016) Effect of heavy metals on seed germination of Trigonella foenum-graceum L. Int J Life-Sci Sci Res 2(4):488–493
Mitra A, Chatterjee S, Gupta DK (2020) environmental arsenic exposure and human health risk. In: Arsenic water resources contamination. Springer, pp 103–129
Müller K, Daus B, Mattusch J, Vetterlein D, Merbach I, Wennrich R (2013) Impact of arsenic on uptake and bio-accumulation of antimony by arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. Environ Poll 174:128–133
Naseer S, Nisar A, Ashraf M (2001) Effect of salt stress on germination and seedling growth of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Pak J Biol Sci 4(3):359–360
Özkara A, Akyıl D, Eren Y, Erdoğmuş SF (2015) Potential cytotoxic effect of Anilofos by using Allium cepaassay. Cytotechnology 67(5):783–791
Patel KP, Patel KM (2013) Cytological changes in Trigonella foenum-graecum (L.) under the cadmium stress. J Life Sci Technol. 1(1):10–13
Pio I, Scarlino A, Bloise E, Mele G, Santoro O, Pastore T, Santoro D (2015) Efficient removal of low-arsenic concentrations from drinking water by combined coagulation and adsorption processes. Sep Purif Technol 147:284–291
Podgorski J, Berg M (2020) Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 368(6493):845–850
Premchandra GS, Saneoha H, Ogata S (1990) Cell membrane stability, an indicator of drought tolerance as affected by applied nitrogen in soybean. J Agr Sci Camb 115:63–66
Rahman Z, Singh VP (2019) The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) [arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)] on the total environment: an overview. Environ Monit Assess 191(7):419
Sagisaka S (1979) The occurrence of peroxide in perennial plant Populus glerica. Plant Physiol 57:308–309
Sarangi BK, Tiwari S, Pandey RA (2014) Efficacy of three different plant species for arsenic phyto-extraction from hydroponic system. Environ Eng Res 19(2):145–149
Silveira GL, Lima MGF, dos Reis GB, Palmieri MJ, Andrade-Vieria LF (2017) Toxic effects of environmental pollutants: Comparative investigation using Allium cepa L. and Lactuca sativa L. Chemosphere 178:359–367
Srivastava S (ed) (2020). Arsenic in drinking water and food. Springer
Stephen J (1979) Cytological cause of spontaneous fruit abortion in Haemanthus katherinal. Cytologia 44:805–812
Suganthi V, Mohamed MMP, Rajalakshmi K (2013) Effect of lead toxicity on growth and antioxidant status in Trigonella foenum-graecum. Elixir Pollut 57:14167–14171
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39
Tripathi P, Mishra A, Dwivedi S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Singh RP, Tripathi RD (2012) Differential response of oxidative stress and thiol metabolism in contrasting rice genotypes for arsenic tolerance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:189–198
Tu C, Ma LQ, Bondada B (2002) Arsenic accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Chinese Brake (Pteris vittata L.) and its utilization potential for phytoremediation. J Environ Qual 31:1671–1675
Van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57e149
Verma S, Srivastava A (2018) Morphotoxicity and cytogenotoxicity of pendimethalin in the test plant Allium cepa L.—A biomarker based study. Chemosphere 206:248–254
Waqas H, Shan A, Khan YG, Nawaz R, Rizwan M, Rehman MSU, Shakoor MB, Ahmed W, Jabeen M (2017) Human health risk assessment of arsenic in groundwater aquifers of Lahore, Pakistan. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 23(4):836–850
Wei X, Zhou Y, Tsang DC, Song L, Zhang C, Yin M, Liu J, Xiao T, Zhang G, Wang J (2020) Hyperaccumulation and transport mechanism of thallium and arsenic in brake ferns (Pteris vittata L.): A case study from mining area. J Hazard Mater 388:121756
Yi H, Wu L, Jiang L (2007) Genotoxicity of arsenic evaluated by Allium-root micronucleus assay. Sci Total Environ 383:232–236
Zeid IM (2001) Responses of Phaseolus vulgaris chromium and cobalt treatments. Biologia Plantarum 44(1):111–115
Zhao FJ, Wang JR, Barker JHA, Schat H, Bleeker PM, McGrath SP (2003) The role of phytochelatins in arsenic tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. New Phytol 159:403–410
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Department of Botany, University of Lucknow, Lucknow for the facilities. Kiran Gupta is thankful to University Grant Commission (UGC), India for the award of Post-doctoral fellowship for women candidate for the financial support. Amit Kumar is thankful to SERB, DST, New Delhi for the award and financial assistance in form of SERB-NPDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Corresponding author and all the co-authors of the MS entitled “Application of Pteris vittata L. for phytoremediation of arsenic and biomonitoring of the process through cyto-genetic biomarkers of Trigonella foenum-graecum L.” have no conflict of interest pertaining to this work being submitted in the journal “journal “Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, K., Srivastava, S., Saxena, G. et al. Application of Pteris vittata L. for phytoremediation of arsenic and biomonitoring of the process through cyto-genetic biomarkers of Trigonella foenum-graecum L.. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 28, 91–106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01124-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01124-4