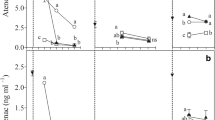
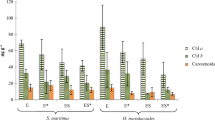
Abstract
Triclosan (TCS) is a halogenated aromatic compound used in household products such as toothpaste, detergents, soaps, and cosmetics, and is frequently found in domestic wastewater. The harmful effects of TCS are associated with hormonal and metabolic alterations in aquatic organisms. The present study evaluated the Phyto-purifying capacity of Cyperus articulatus L. planted in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland used for domestic wastewater treatment. This required the usage of a 0.8 m × 0.5 m and 0.85 m high artificial wetland in fiberglass and polyester resin filled with garden gravel to a depth of 0.4 m, which received a daily flow of 18 L from a storage tank for 4 months. The concentration of TCS in influent and effluent water, as well as in plant roots and stems, was determined by gas chromatography coupled to a mass spectrometer. The TCS removal efficiency was 63% and was lower than that reported in similar studies. The translocation factor (TF) and bio-concentration factor (BCF) reached values of 1 and 0.06, respectively, indicating that C. articulatus can absorb and transport TCS from the root to higher parts of the stem. The results of this study lead to the conclusion that a local plant such as C. articulatus planted in constructed wetlands can decrease the concentration of an emerging pollutant, such as TCS, from domestic wastewater.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data that support the findings of this study have been deposited in https://www.hydroshare.org/home//.
References
Al-Farsi, R. S., Ahmed, M., Al-Busaidi, A., & Choudri, B. S. (2017). Translocation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) into plant tissues: A review. Emerging Contaminants. KeAi Communications Co. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2018.02.001
Ansari, A. A., Gill, S. S., Gill, R., Lanza, G. R., & Newman, L. (2015). Phytoremediation. (A. A. Ansari, S. S. Gill, R. Gill, G. R. Lanza, & L. Newman, Eds.). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10395-2
APHA-AWWA-WEF. (2012). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater (22nd ed.). American Public Health Association.
Ávila, C., Nivala, J., Olsson, L., Kassa, K., Headley, T., Mueller, R. A., … García, J. (2014). Emerging organic contaminants in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Influence of media size, loading frequency and use of active aeration. Science of the Total Environment, 494–495, 211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.128
Baker, A. J. M., & Brooks, R. R. (1989). Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements - A review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery, 1(2), 81–126.
Barbosa, M. O., Moreira, N. F. F., Ribeiro, A. R., Pereira, M. F. R., & Silva, A. M. T. (2016, May). Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: An overview of the watch list of EU Decision 2015/495. Water Research. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.02.047
Bedoya-Ríos, D. F., Lara-Borrero, J. A., Duque-Pardo, V., Madera-Parra, C. A., Jimenez, E. M., & Toro, A. F. (2018). Study of the occurrence and ecosystem danger of selected endocrine disruptors in the urban water cycle of the city of Bogotá, Colombia. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 53(4), 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2017.1401372
Burgos, V., Araya, F., Vera, I., & Vidal, G. (2017). Performance of ornamental plants in mesocosm subsurface constructed wetlands under different organic sewage loading. Ecological Engineering, 99, 246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.058
Button, M., Cosway, K., Sui, J., & Weber, K. (2019). Impacts and fate of triclosan and sulfamethoxazole in intensified re-circulating vertical flow constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 649, 1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.395
Carter, L. J., Harris, E., Williams, M., Ryan, J. J., Kookana, R. S., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2014). Fate and uptake of pharmaceuticals in soil-plant systems. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(4), 816–825. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404282y
Caselles-Osorio, A., Vega, H., Lancheros, J. C., Casierra-Martínez, H. A., & Mosquera, J. E. (2017). Horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetland removal efficiency using Cyperus articulatus L. Ecological Engineering, 99, 479–485.
Caselles-Osorio, A., Villafañe, P., Caballero, V., & Manzano, Y. (2011). Efficiency of mesocosm-scale constructed wetland systems for treatment of sanitary wastewater under tropical conditions. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 220(1–4), 161–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0743-7
Casierra-Martínez, H. A., Charris-Olmos, J. C., Caselles-Osorio, A., & Parody-Muñoz, A. E. (2017). Organic matter and nutrients removal in tropical constructed wetlands using Cyperus ligularis (Cyperaceae) and Echinocloa colona (Poaceae). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228(9). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3531-1
Casierra-Martinez, H. A., Madera-Parra, C. A., Vargas-Ramírez, X. M., Caselles-Osorio, A., & Torres-López, W. A. (2020). Diclofenac and carbamazepine removal from domestic wastewater using a Constructed Wetland-Solar Photo-Fenton coupled system. Ecological Engineering, 153(December 2019), 105699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105699
Cassia, R. De, Queiroz, S. De, Maranduba, H. L., Hafner, M. B., Rodrigues, L. B., Adolfo, J., & Neto, D. A. (2020). Life cycle thinking applied to phytoremediation of dairy wastewater using aquatic macrophytes for treatment and biomass production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 122006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122006
Charris, J. C., & Caselles-Osorio, A. (2016). Eficiencia de eliminación de contaminantes del agua residual doméstica con humedales construidos experimentales plantados con Cyperus ligularis (Cyperaceae) y Echinochloa colonum (Poaceae). Tecnologia y Ciencias Del Agua, 7(6), 93–103.
Chen, X., Gu, X., Bao, L., Ma, S., & Mu, Y. (2021). Comparison of adsorption and desorption of triclosan between microplastics and soil particles. Chemosphere, 263, 127947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127947
Chen, Yan, Lu, Y., Nie, E., Kashif, A., Zhang, S., Ye, Q., & Wang, H. (2020). Uptake, translocation and accumulation of the fungicide benzene kresoxim-methyl in Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica campastris var. parachinensis) and water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica). Environmental Pollution, 264, 114815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114815
Chen, Yi., Vymazal, J., Březinová, T., Koželuh, M., Kule, L., Huang, J., & Chen, Z. (2016). Occurrence, removal and environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in rural wastewater treatment wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 566–567, 1660–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.069
Coogan, M. A., Edziyie, R. E., La Point, T. W., & Venables, B. J. (2007). Algal bioaccumulation of triclocarban, triclosan, and methyl-triclosan in a North Texas wastewater treatment plant receiving stream. Chemosphere, 67(10), 1911–1918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.027
Dai, Y., Tao, N. V., Tai, R., Ping, Y., Tam, N. F., Yee Dan, A., & Yang, Y. (2017). Application of a full-scale newly developed stacked constructed wetland and an assembled bio-filter for reducing phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals from secondary effluent. Ecological Engineering, 99, 496–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.007
Delgado, Y. (2019). Diagnóstico y remoción de contaminantes emergentes en aguas superficiales y cloacales. lLA PLATA, ARGENTINA. Universidad Nacional de La Plata
Dhillon, G. S., Kaur, S., Pulicharla, R., Brar, S. K. (2015). Triclosan : Current status , occurrence , environmental risks and bioaccumulation potential, 5657–5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120505657
Dodgen, L. K., Ueda, A., Wu, X., Parker, D. R., & Gan, J. (2015). Effect of transpiration on plant accumulation and translocation of PPCP/EDCs. Environmental Pollution, 198, 144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.002
Dordio, Ana, Carvalho, A. J. P., Teixeira, D. M., Dias, C. B., & Pinto, A. P. (2010). Removal of pharmaceuticals in microcosm constructed wetlands using Typha spp. and LECA. Bioresource Technology, 101(3), 886–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.001
Dordio, A. V., & Carvalho, A. J. P. (2013). Organic xenobiotics removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of the support matrix. Journal of Hazardous Materials. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.008
Duque, P. V. (2016). Capacidad de los humedales naturales para remover disruptores endocrinos del ciclo urbano del agua. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana.
Durán-Domínguez, M. del C. de B., Enrique, N.-F. A., & Bayona, J. M. (2018). Artificial or constructed wetlands: A suitable technology for sustainable water management. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group (ilustrada). https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315184265
Ebrahim, M., Gaber, Y., El-reash, A., Ahmed, M. I., & Rizk, F. W. (2020). Effect of media variation on the removal e ffi ciency of pollutants from domestic wastewater in constructed wetland systems. Ecological Engineering, 143(November 2019), 105668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105668
Farrag, H. F., & Fawzy, M. (2012). Phytoremediation potentiality of Cyperus articulatus L. Life Science Journal 9
FDA, U. . F. & D. A. (2016). Rule removes triclosan and triclocarban from over-the-counter antibacterial hand and body washes. Available on: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-issues-final-rule-safety-and-effectiveness-antibacterial-soaps. Reviewed. Septiemrbe 28 2021
Flora-of-North-America. (1993). Flora of North America: Volume. 23: Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in Part): Cyperaceae, vol. 23 (Committee)
Francini, A., Mariotti, L., Di Gregorio, S., Sebastiani, L., & Andreucci, A. (2018). Removal of micro-pollutants from urban wastewater by constructed wetlands with Phragmites australis and Salix matsudana. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(36), 36474–36484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3582-x
Gaffney, V., Cardoso, V., Rodrigues, Alexandre Ferreira, E., & Benoliel, Maria. Almeida, C. (2014). Analise De Farmacos Em Águas Por SPE-UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Quim. Nova, 37(1), 138–149.
Galal, T. M., Gharib, F. A., Ghazi, S. M., & Mansour, K. H. (2017). Metal uptake capability of Cyperus articulatus L. and its role in mitigating heavy metals from contaminated wetlands. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(27), 21636–21648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9793-8
Gao, J., Zhao, J., Zhang, J., Li, Q., Gao, J., Cai, M., & Zhang, J. (2020). Preparation of a new low-cost substrate prepared from drinking water treatment sludge (DWTS)/bentonite/zeolite/fly ash for rapid phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. Journal of Cleaner Production, 261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121110
Gil, J. M., María Soto, A., Iván Usma, J., & Darío Gutiérrez, O. (2012). Emerging contaminants in waters: effects and possible treatments Contaminantes emergentes em águas, efeitos e possíveis tratamentos. Producción+Limpia, 7(2)
Hashmi, M. Z. (2020). Antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance genes environmental occurrence and treatment technologies. Springer International Publishing.
He, Y., Nie, E., Li, C., Ye, Q., & Wang, H. (2016). Uptake and subcellular distribution of triclosan in typical hydrophytes under hydroponic conditions. Environmental Pollution, 220, 400–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.076
Hijosa-Valsero, M., Matamoros, V., Sidrach-Cardona, R., Martín-Villacorta, J., Bécares, E., & Bayona, J. M. (2010). Comprehensive assessment of the design configuration of constructed wetlands for the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from urban wastewaters. Water Research, 44(12), 3669–3678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.04.022
Hu, X., Xie, H., Zhuang, L., Zhang, J., Hu, Z., Liang, S., & Feng, K. (2021). A review on the role of plant in pharmaceuticals and personal care products ( PPCPs ) removal in constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 780, 146637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146637
Ilyas, H., & van Hullebusch, E. D. (2020). Performance comparison of different constructed wetlands designs for the removal of personal care products. International Journal of Environmental and Research and Publich Health, 17, 3091.
Kadlec, R. H., & Wallace, S. D. (2009). Treatment wetlands. (C. Press, Ed.), Treatment wetlands (Second Edi). Boca Ratón, Florida. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420012514
Kadlec, R., & Wallace, S. (2009b). Treatment wetlands (Second edi). CRC Press Taylo & Francis Group.
Konnerup, D., Koottatep, T., & Brix, H. (2009). Treatment of domestic wastewater in tropical, subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with Canna and Heliconia. Ecological Engineering, 35(2), 248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.04.018
Lancheros, J. C., Madera-Parra, C. A., Caselles-Osorio, A., Torres-López, W. A., & Vargas-Ramírez, X. M. (2019). Ibuprofen and Naproxen removal from domestic wastewater using a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland coupled to ozonation. Ecological Engineering, 135(October 2018), 89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.05.007
Lasat, M. M., Pence, N. S., Garvin, D. F., Ebbs, S. D., & Kochian, L. V. (2000). Molecular physiology of zinc transport in the Zn hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Journal of Experimental Botany, 51(342), 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.342.71
Lei, Y., Langenhoff, A., Bruning, H., & Rijnaarts, H. (2021). Sorption of micropollutants on selected constructed wetland support matrices. Chemosphere, 275, 130050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130050
Leto, C., Tuttolomondo, T., La Bella, S., Leone, R., & Licata, M. (2013). Effects of plant species in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland - Phytoremediation of treated urban wastewater with Cyperus alternifolius L. and Typha latifolia L. in the West of Sicily (Italy). Ecological Engineering, 61, 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.09.014
Li, H., & Tao, W. (2017). Efficient ammonia removal in recirculating vertical flow constructed wetlands : Complementary roles of anammox and denitrification in simultaneous nitritation, anammox and denitrification process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 317, 972–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.143
Li, J., Zhou, Q., & Campos, L. C. (2017). Removal of selected emerging PPCP compounds using greater duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) based lab-scale free water constructed wetland. Water Research, 126, 252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.002
Liu, J., Wang, J., Zhao, C., Hay, A. G., & Xie, H. (2015). Triclosan removal in wetlands constructed with different aquatic plants. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7063-6
Llanos-Lizcano, A., Barraza, E., Narvaez, A., Varela, L., & Caselles-Osorio, A. (2019). Efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands and microbial community composition operating under tropical conditions. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21(1), 34–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1523874
Luo, Y., Guo, W., Ngo, H. H., Nghiem, L. D., Hai, F. I., Zhang, J., … Wang, X. C. (2014). A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 473–474, 619–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065
Lv, S., Zhou, Z., Xue, M., Zhang, X., & Yang, Z. (2020). Adsorption characteristics of reactive blue 81 by powdered activated carbon : Role of the calcium content. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 36(February), 101247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101247
Matamoros, V., & Bayona, J. M. (2006). Elimination of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(18), 5811–5816. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0607741
Matamoros, V., García, J., & Bayona, J. M. (2008). Organic micropollutant removal in a full-scale surface flow constructed wetland fed with secondary effluent. Water Research, 42(3), 653–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.016
Matamoros, V., Rodríguez, Y., & Bayona, J. M. (2017). Mitigation of emerging contaminants by full-scale horizontal flow constructed wetlands fed with secondary treated wastewater. Ecological Engineering, 99, 222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.054
Matamoros, V., Xuan, L., Arias, C. A., Salvadó, V., & Brix, H. (2012). Evaluation of aquatic plants for removing polar microcontaminants : A microcosm experiment. Chemosphere, 88, 1257–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.04.004
Medina, M., Katy, D., Montano, C. Y. N. (2014). “DETERMINACIÓN DEL FACTOR DE BIOCONCENTRACIÓN Y TRASLOCACIÓN DE METALES PESADOS EN EL Juncus arcticus Willd. Y Cortaderia rudiuscula Stapf, DE ÁREAS CONTAMINADAS CON EL PASIVO AMBIENTAL MINERO ALIANZA - ANCASH 2013.” UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL “SANTIAGO ANTÚNEZ DE MAYOLO” FACULTAD DE CIENCIAS DEL AMBIENTE ESCUELA ACADÉMICO PROFESIONAL DE INGENIERIA AMBIENTAL “DETERMINACIÓN.
Mlih, R., Bydalek, F., Klumpp, E., Yaghi, N., Bol, R., Wenk, J., … Str, W. J. (2020). Light-expanded clay aggregate ( LECA ) as a substrate in constructed wetlands – A review. Ecological Engineering, 148(February), 105783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.105783
Nie, E., Chen, Y., Gao, X., Chen, Y., Ye, Q., & Wang, H. (2020). Uptake, translocation and accumulation of 14C-triclosan in soil-peanut plant system. Science of the Total Environment, 724, 138165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138165
Olguín, E. J., Sánchez-Galván, G., González-Portela, R. E., Domínguez, J. L., Hernández, V. J., & Castillo, O. S. (2014). The use of floating wetlands with Cyperus papyrus and Pontederia sagittata for the treatment of a polluted urban lake. In Memorias de La Segunda Conferencia Panamericana En Sistemas de Humedales Para El Manejo, Tratamiento y Mejoramiento de La Calidad Del Agua.IMTA, Morelia, 45–47
Pi, N., Ng, J. Z., & Kelly, B. C. (2017). Bioaccumulation of pharmaceutically active compounds and endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquatic macrophytes : Results of hydroponic experiments with Echinodorus horemanii and Eichhornia crassipes. Science of the Total Environment, 602(1), 812–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.137
Prosser, R. S., Lissemore, L., Topp, E., & Sibley, P. K. (2014). Bioaccumulation of triclosan and triclocarban in plants grown in soils amended with municipal dewatered biosolids. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 33(5), 975–984. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2505
Quan, B., Li, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., Ming, Y., & Huang, Y. (2019). Technology and principle of removing triclosan from aqueous media : A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 378(April), 122185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122185
Ramírez, M. L. G. (2009). Determinación de pesticidas en vegetales mediante cromatografía de gases- espectrometría de masa/masa (GC-MS/MS). UNIVERSIDAD TECNOLÓGICA DE LA MIXTECA
Ramprasad, C., & Philip, L. (2017). Contributions of various processes to the removal of surfactants and personal care products in constructed wetland. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.106
Reddy, K. R., & DeLaune, R. D. (2008). Biochemistry of wetlands. Science and applications. CRC Press Taylo & Francis Group.
Reinoso, J. del C., Serrano, C. Y., & Orellana, D. F. (2017). Contaminantes emergentes y su impacto en la salud. Emerging contaminants and its impact on the health. Revista de La Facultad de Ciencias Médicas de La Universidad de Cuenca, 35(2), 55–59
Rodriguez, D. J., Serrano, H. A., Delgado, A., Nolasco, D., & Saltiel, G. (2020). From waste to resource. Shifting paradigms for smarter wastewater interventions in Latin America and the Caribbean
Romero-Hernández, J. A., Amaya-Chávez, A., Balderas-Hernández, P., Roa-Morales, G., González-Rivas, N., & Balderas-Plata, M. Á. (2017). Tolerance and hyperaccumulation of a mixture of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Hg, and Zn) by four aquatic macrophytes. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 19(3), 239–245. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1207610
Soda, S., Hamada, T., Yamaoka, Y., Ike, M., Nakazato, H., Saeki, Y., … Sakurai, Y. (2012). Constructed wetlands for advanced treatment of wastewater with a complex matrix from a metal-processing plant : Bioconcentration and translocation factors of various metals in Acorus gramineus and Cyperus alternifolius. Ecological Engineering, 39, 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.11.014
Vymazal, J. (2004). Removal of phosphorus of constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow in the Czech Republic. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 4, 657–670.
Vymazal, J., & Brezinová, T. (2015). Heavy metals in plants in constructed and natural wetlands : Concentration, accumulation and seasonality. Water Science & Technology, 71(2), 268–276. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.507
Vystavna, Y., Frkova, Z., Marchand, L., Vergeles, Y., & Stolberg, F. (2017). Removal efficiency of pharmaceuticals in a full scale constructed wetland in East Ukraine. Ecological Engineering, 108, 50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.08.009
Walaszek, M., del Nero, M., Bois, P., Ribstein, L. C. O., Wanko, A., & L. J. (2018). Sorption behavior of copper, lead and zinc by a constructed wetland treating urban stormwater. Applied Geochemistry, 97, 167–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.08.019
Wang, T. T., Ying, G. G., Shi, W. J., Zhao, J. L., Liu, Y. S., Chen, J., … Xiong, Q. (2020). Uptake and translocation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) by wetland plants: Tissue- and cell-level distribution visualization with desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (DESI-MS) and transmission El. Environmental Science and Technology, 54(10), 6009–6020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05160
Westerhoff, P., Sharif, F., Halden, R., Herckes, P., & Krajmalnik-Brown, R. (2014). Constructed wetlands for treatment of organic and engineered nanomaterial contaminants of emerging concerns. Water Research Foundation.
Xie, H., Yang, Y., Liu, J., Kang, Y., Zhang, J., Hu, Z., & Liang, S. (2018). Enhanced triclosan and nutrient removal performance in vertical up-flow constructed wetlands with manganese oxides. Water Research, 143, 457–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.061
Ying, G. G., & Kookana, R. S. (2007). Triclosan in wastewaters and biosolids from Australian wastewater treatment plants. Environment International, 33(2), 199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.09.008
Zarate, F. M., Schulwitz, S. E., Stevens, K. J., & Venables, B. J. (2012). Bioconcentration of triclosan, methyl-triclosan, and triclocarban in the plants and sediments of a constructed wetland. Chemosphere, 88(3), 323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.005
Zhai, J., He, Q., & Kejia, N. (2012). Variation of dissolved oxygen and redox potential and their correlation with microbial population along a novel horizontal subsurface flow wetland, (September). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.655320
Zhang, D., Gersberg, R. M., Ng, W. J., & Tan, S. K. (2014). Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic plant-based systems: A review. Environmental Pollution. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.009
Zhang, D. Q., Hua, T., Gersberg, R. M., Zhu, J., Ng, W. J., & Tan, S. K. (2012). Fate of diclofenac in wetland mesocosms planted with Scirpus validus. Ecological Engineering, 49, 59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.08.018
Zhang, D. Q., Tan, S. K., Gersberg, R. M., Sadreddini, S., Zhu, J., & Tuan, N. A. (2011). Removal of pharmaceutical compounds in tropical constructed wetlands. Ecological Engineering, 37(3), 460–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.11.002
Zhao, C., Xie, H. J., Xu, J., Zhang, J., Liang, S., Hao, J., … Wang, J. (2016). Removal mechanisms and plant species selection by bioaccumulative factors in surface flow constructed wetlands (CWs): In the case of triclosan. Science of the Total Environment, 547, 9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.119
Zhu, H., Yan, B., Xu, Y., Guan, J., & Liu, S. (2014). Removal of nitrogen and COD in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands under different influent C/N ratios. Ecological Engineering, 63, 58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.12.018
Zhu, T., & Sikora, F. J. (1995). Ammonium and nitratate removal in vegetatedand unvegetated gravel bed microcosm wetlands. Water Science & Technology, 32(3), 1995.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Gabriel Rueda from (Triple A S.A. E.S.P Barranquilla Colombia) for his fundamental support on the development of this research, through his kind advice and accompaniment in the analysis and quantification stage of the study substance. Thank you to engineer Juan Camilo Lancheros and biologist Andrea Jiménez for supporting the figures edition and careful revision of the English, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C-O and E.N-R; methodology, A.C-O, A.O.H, and E.N-R; validation, A.C-O; formal analysis, J.C.M and A.C-O; investigation, E.N-R.; writing-original draft preparation, E.N-R and A.C-O; writing-review and editing, A.C-O and E.N-R; visualization, A.C-O; supervision, A.-C-O; project administration, A.O.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noriega-Rico, E.A., Caselles-Osorio, A., Ortega Herrera, A. et al. Uptake and Accumulation of Triclosan in Cyperus articulatus L. Planted in a Constructed Wetland for the Treatment of Domestic Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05413-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05413-8