Bless Seed
(Nigella sativa)
“Black seed is an all illnesses cure, but death” Mohammed - messenger of the lord
Modern natural distribution of Nigella species in the Old World: 100% white: 0 species, 100% red: 9 species. Map source: SPIESS (2002); distribution data and species delimitations according to ZOHARY (1983).
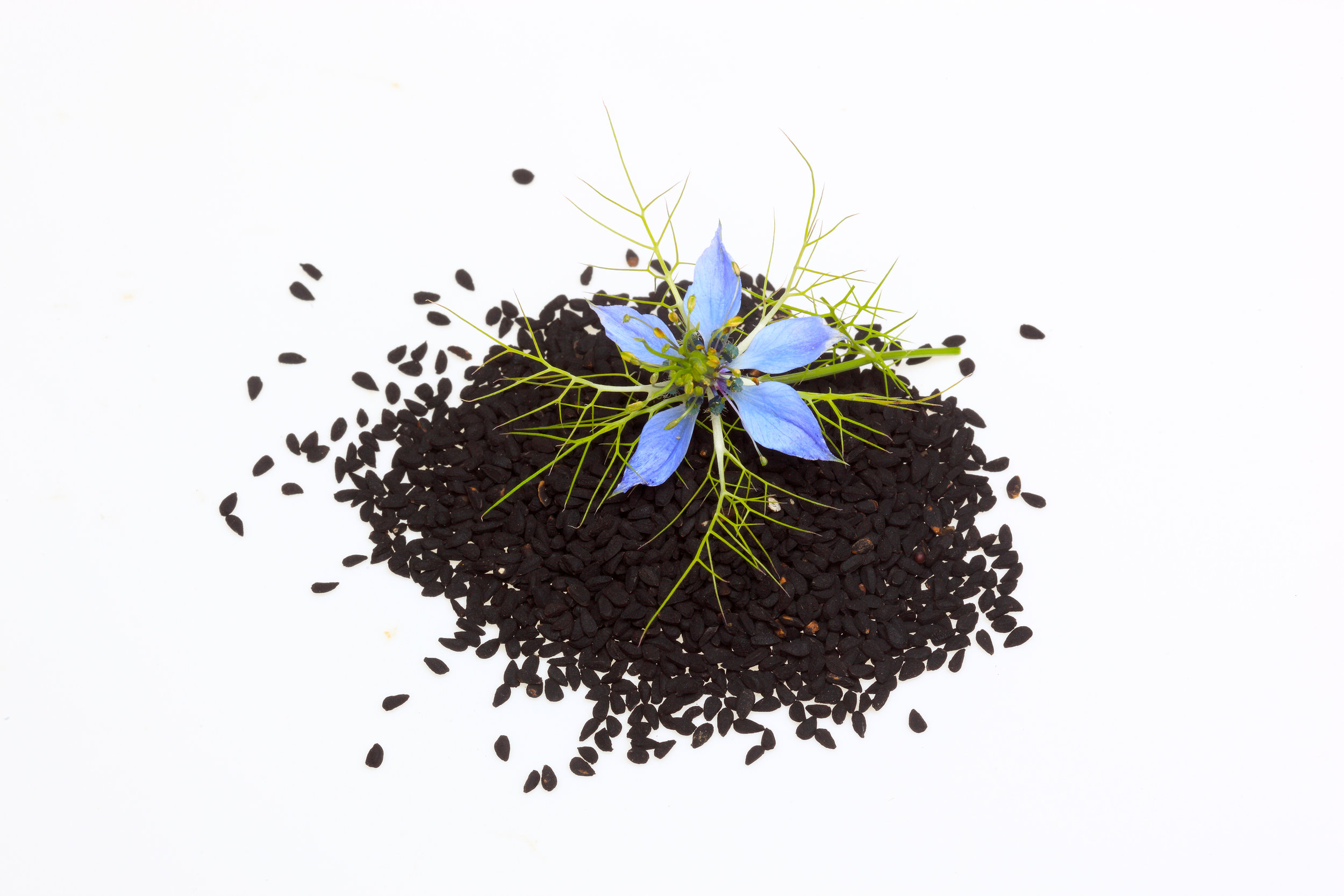
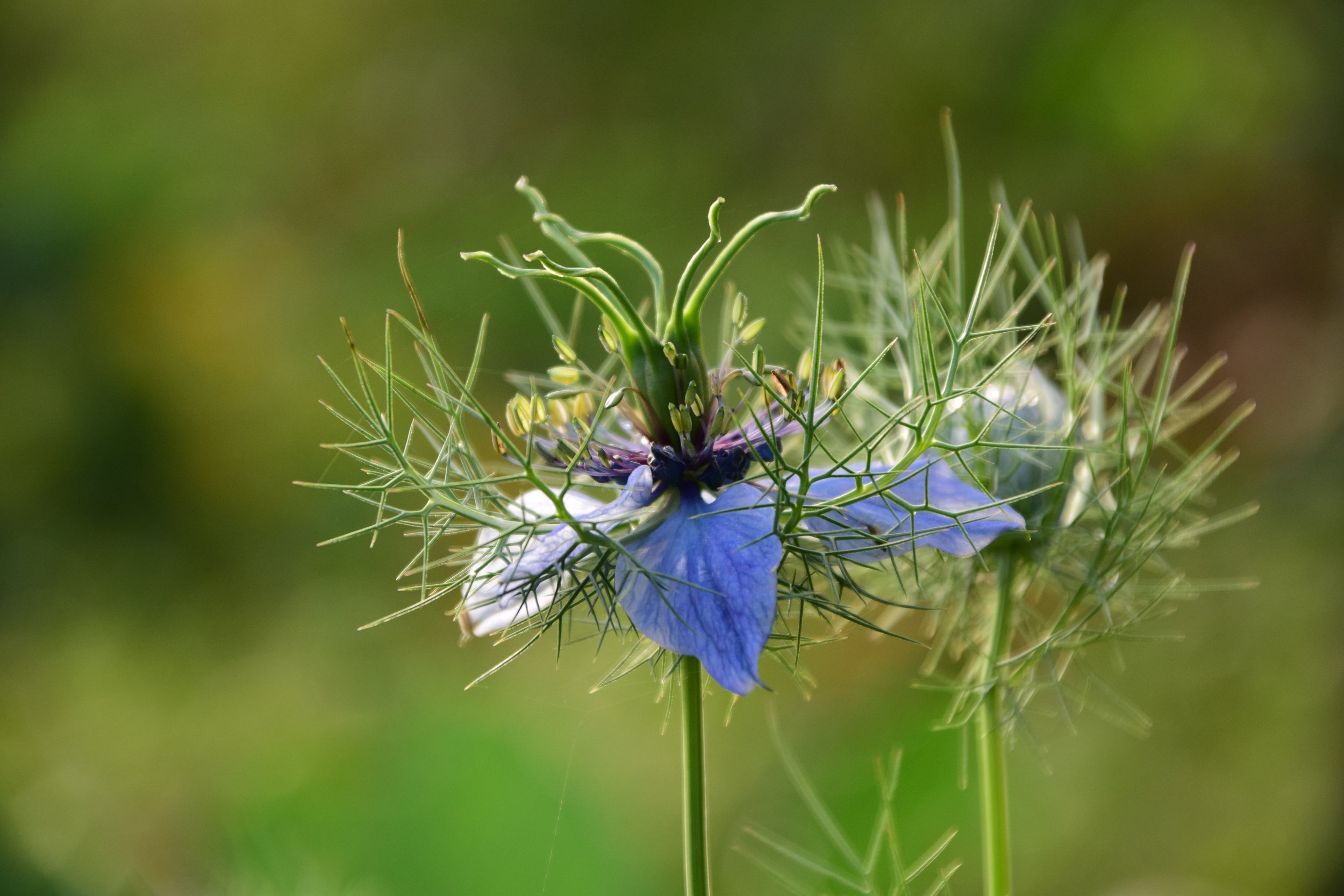
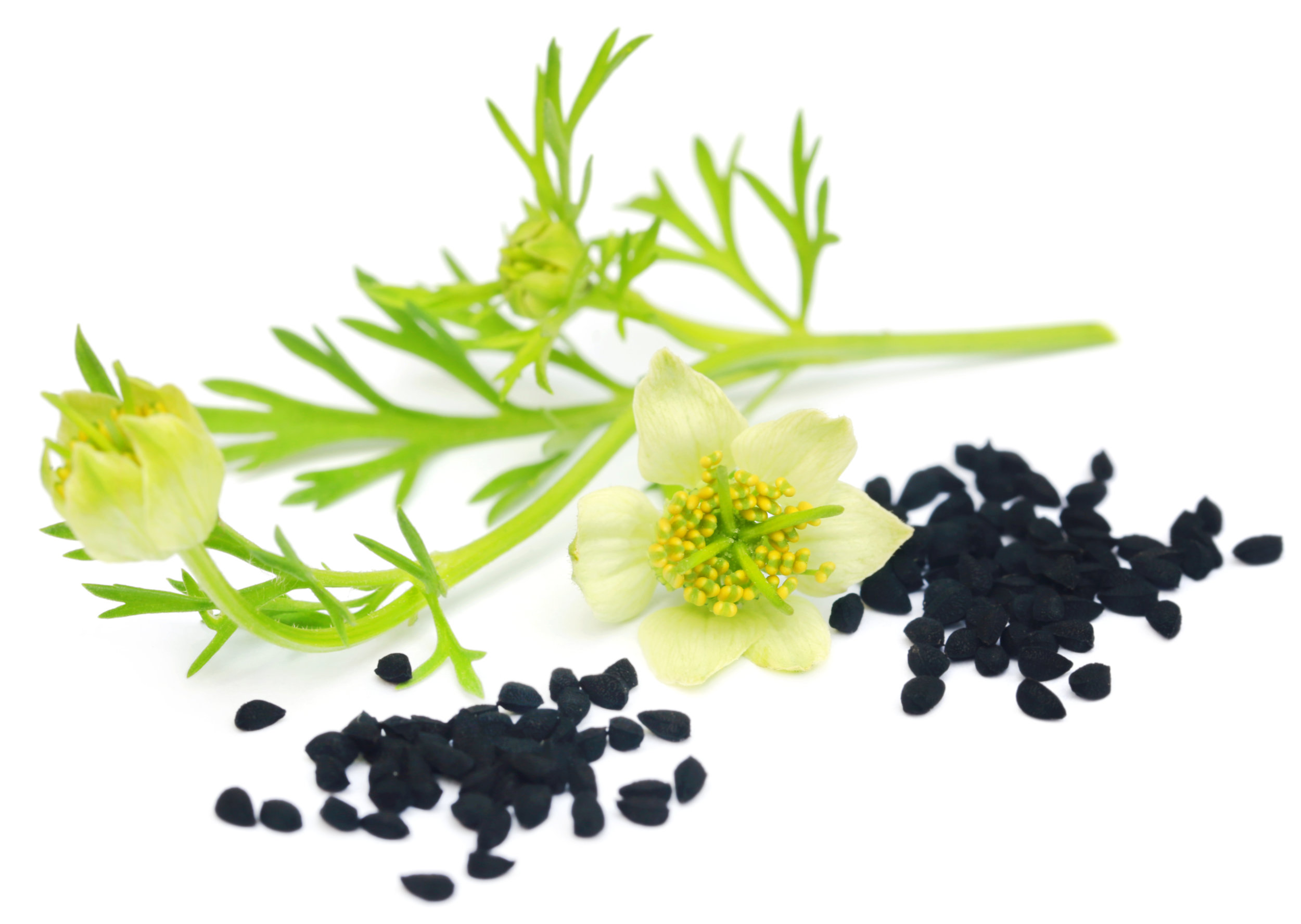
Nigella sativa flower and seeds
Nigella is a genus of 18 species of annual plants in the family Ranunculaceae, native to Mediterranean and southwest Asia.
Nigella sativa has a long history in tradition medicine in different civilizations, recognized as a “miracle cure” for its ability to treat various diseases and assist the body in its own natural healing process.
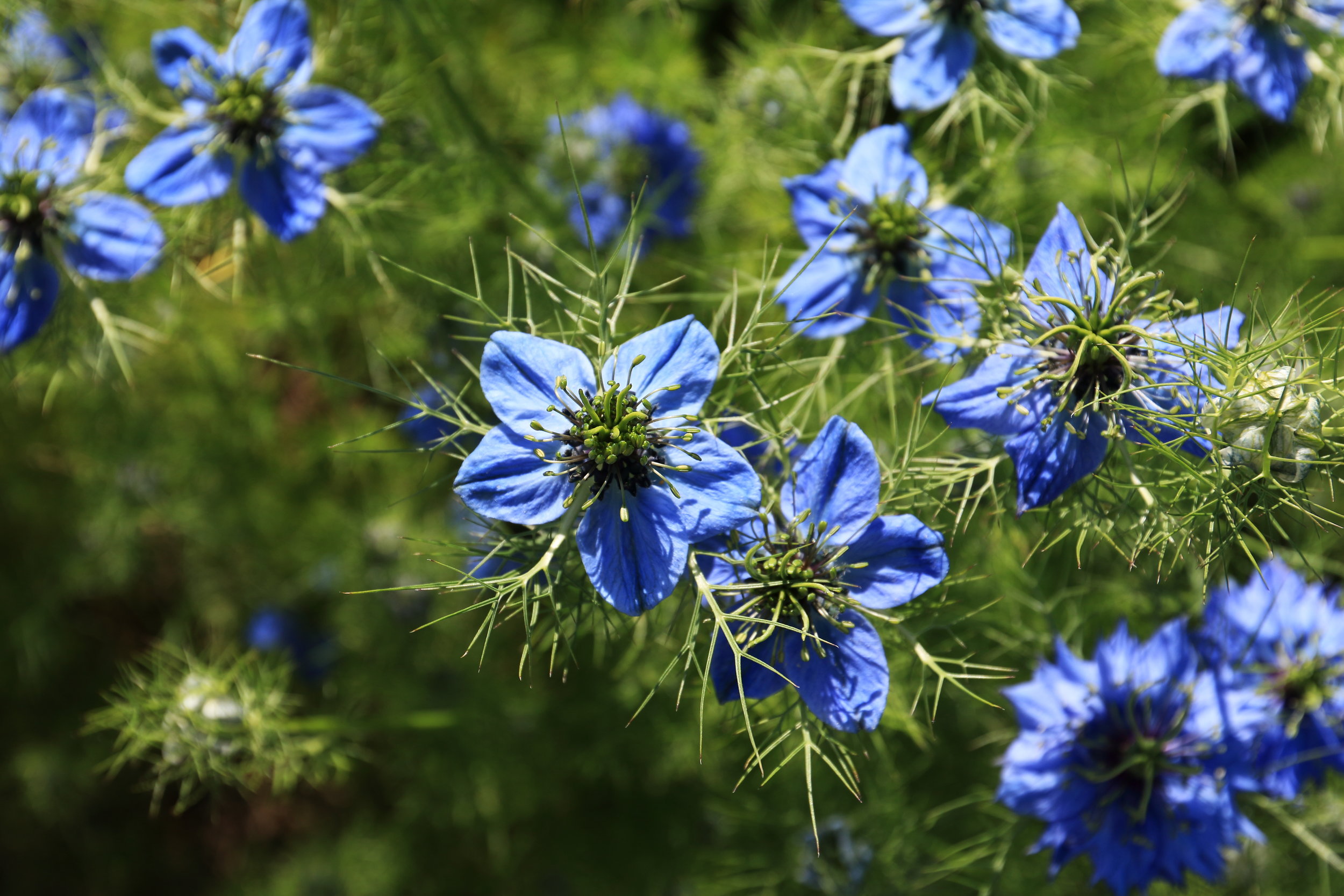
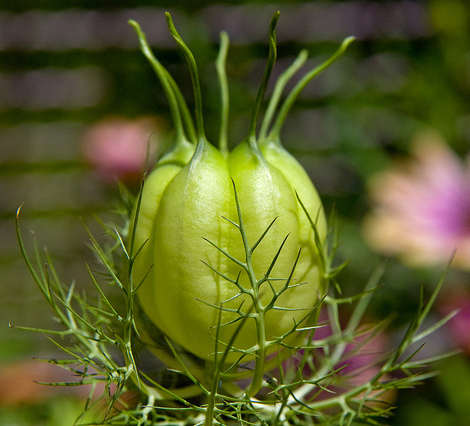
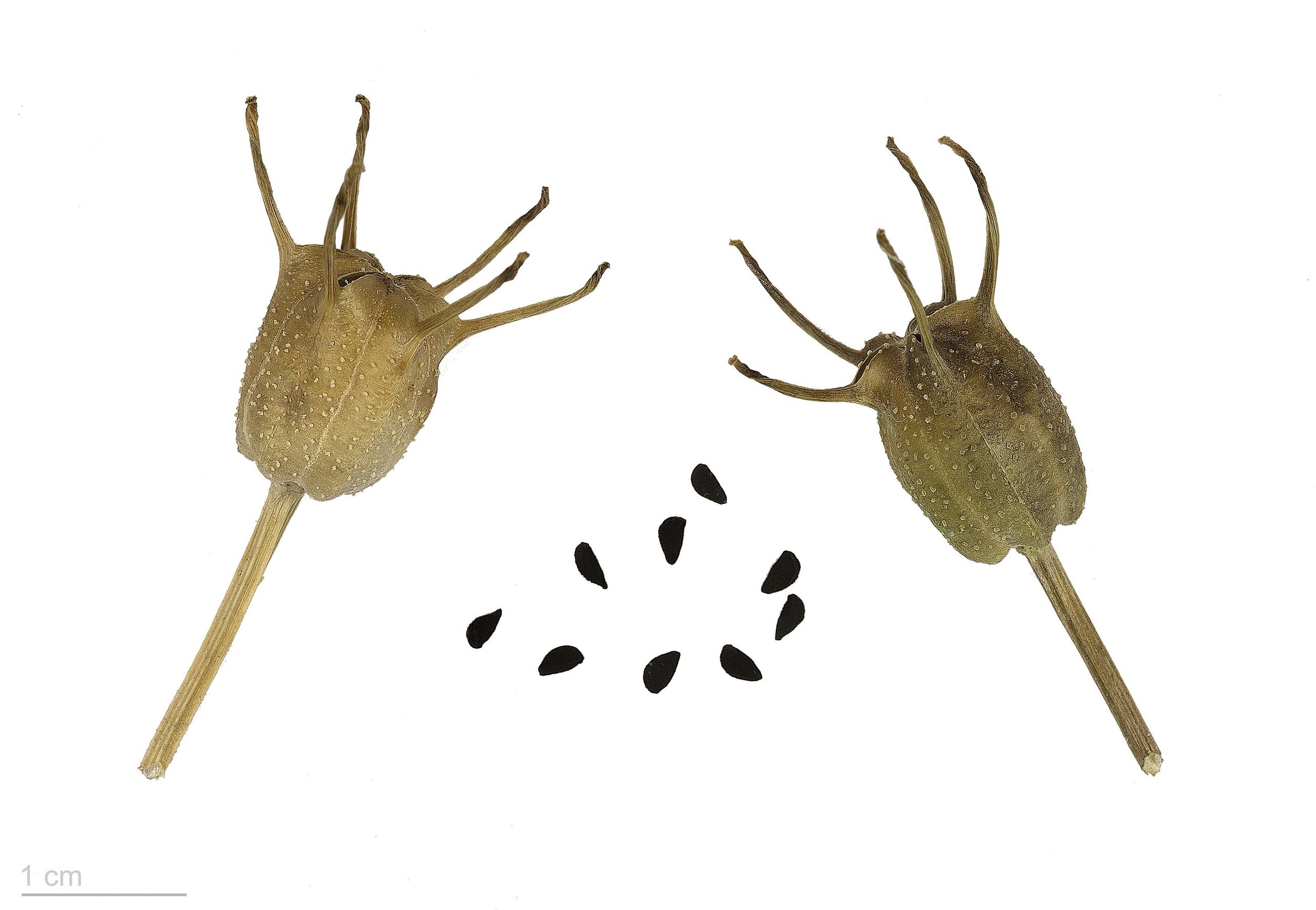
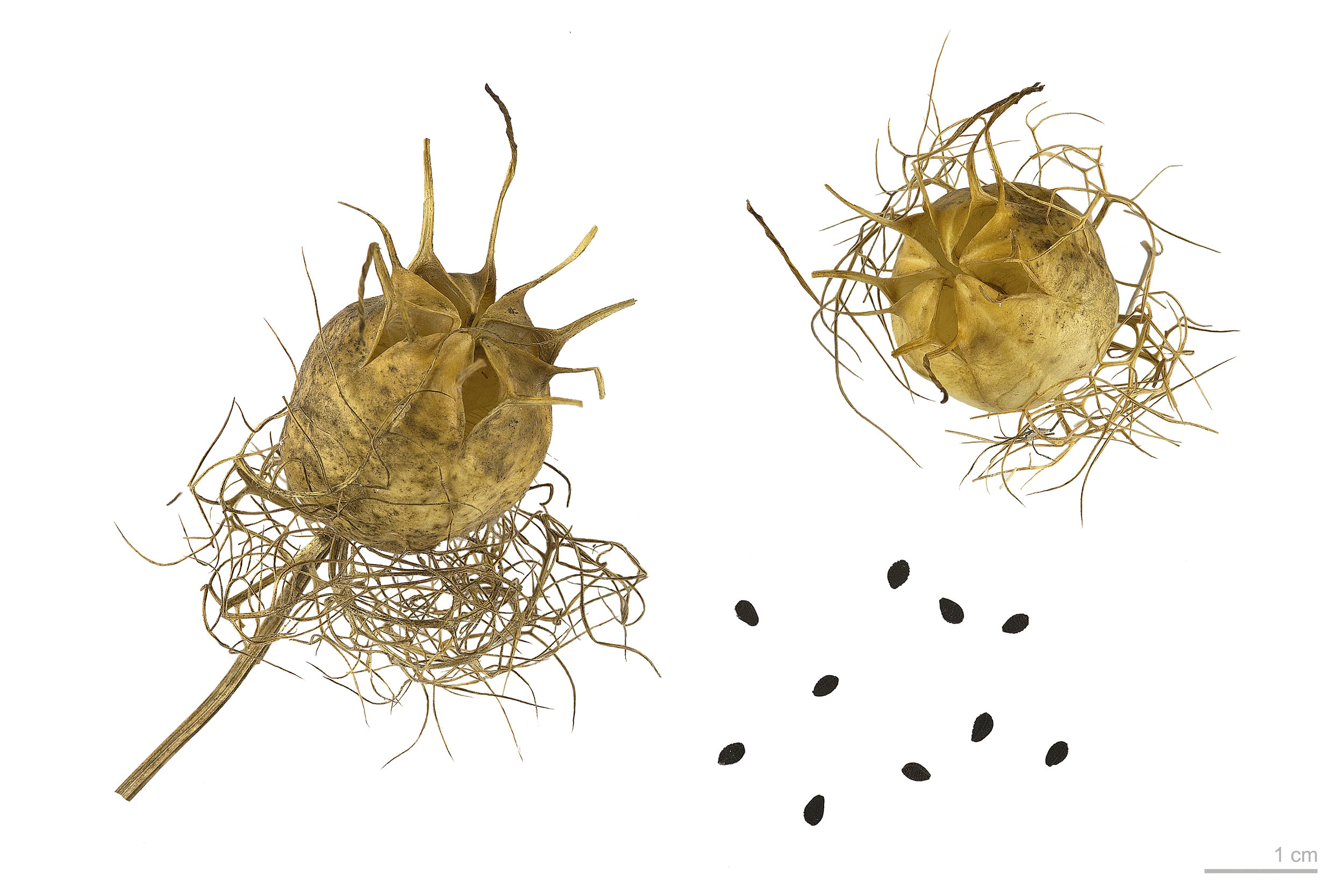
Usually grow to 20–90 cm, threadlike leaves. Flowers could be white, yellow, pink, pale blue or pale purple, with five to 10 petals (characteristically 5 petals and 5 sepals in N. sativa). The fruit (seeds capsule) is a multi-follicular compartment, each contains many seeds.
The aromatic seed contains about 0.5-1.5% essential oil and 35% fatty oil.
The ripe Nigella sativa seed is anthelmintic, carminative, diaphoretic, digestive, diuretic, emmenagogue, galactagogue, laxative and stimulant. An infusion is used in the treatment of digestive and menstrual disorders, insufficient lactation and bronchial complaints.
Externally, Nigella sativa powder, is used to treat abscesses, haemorrhoid and orchitis and to remove lice from the hair.
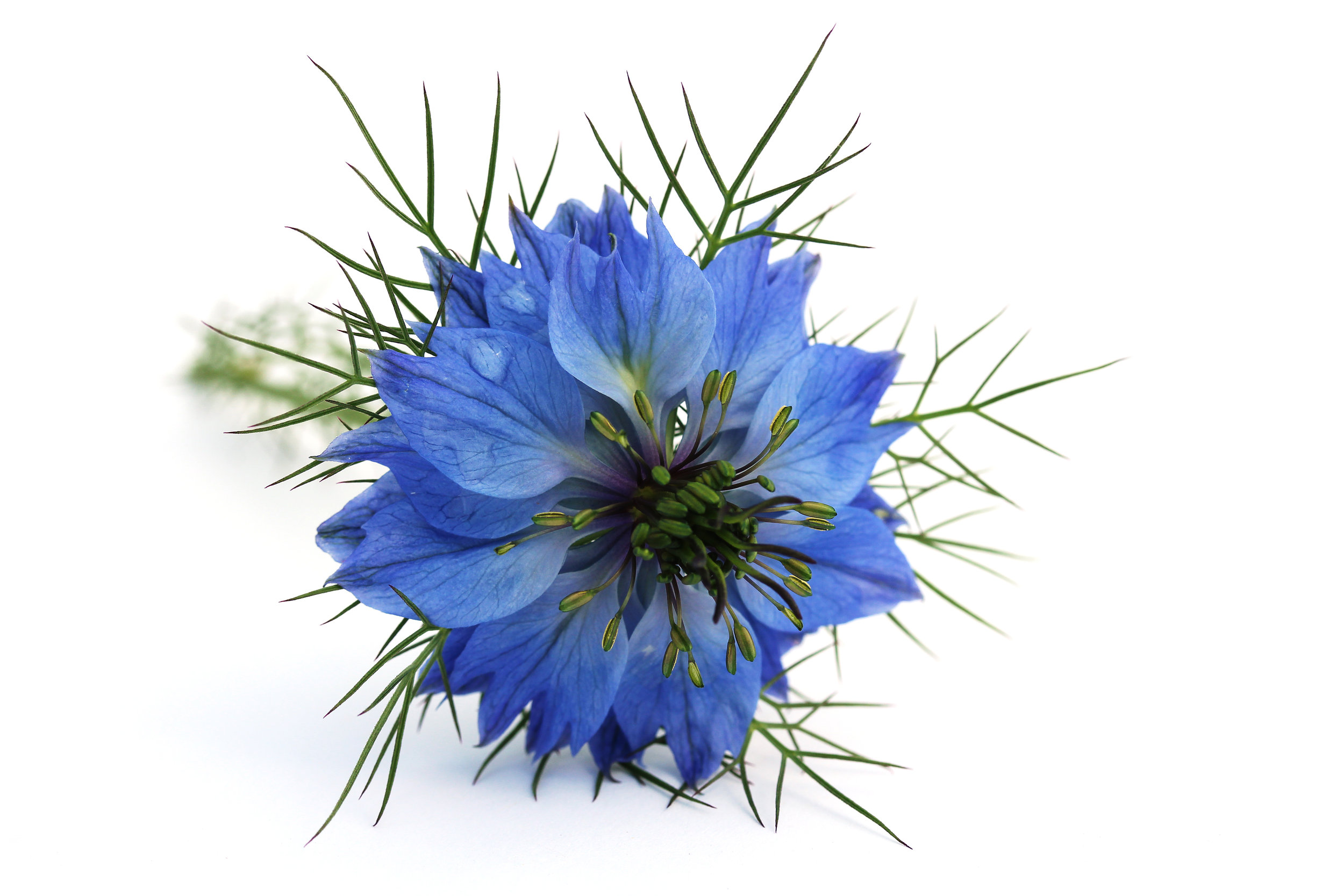
Nigella damascena
Commonly confused for Nigella sativa.
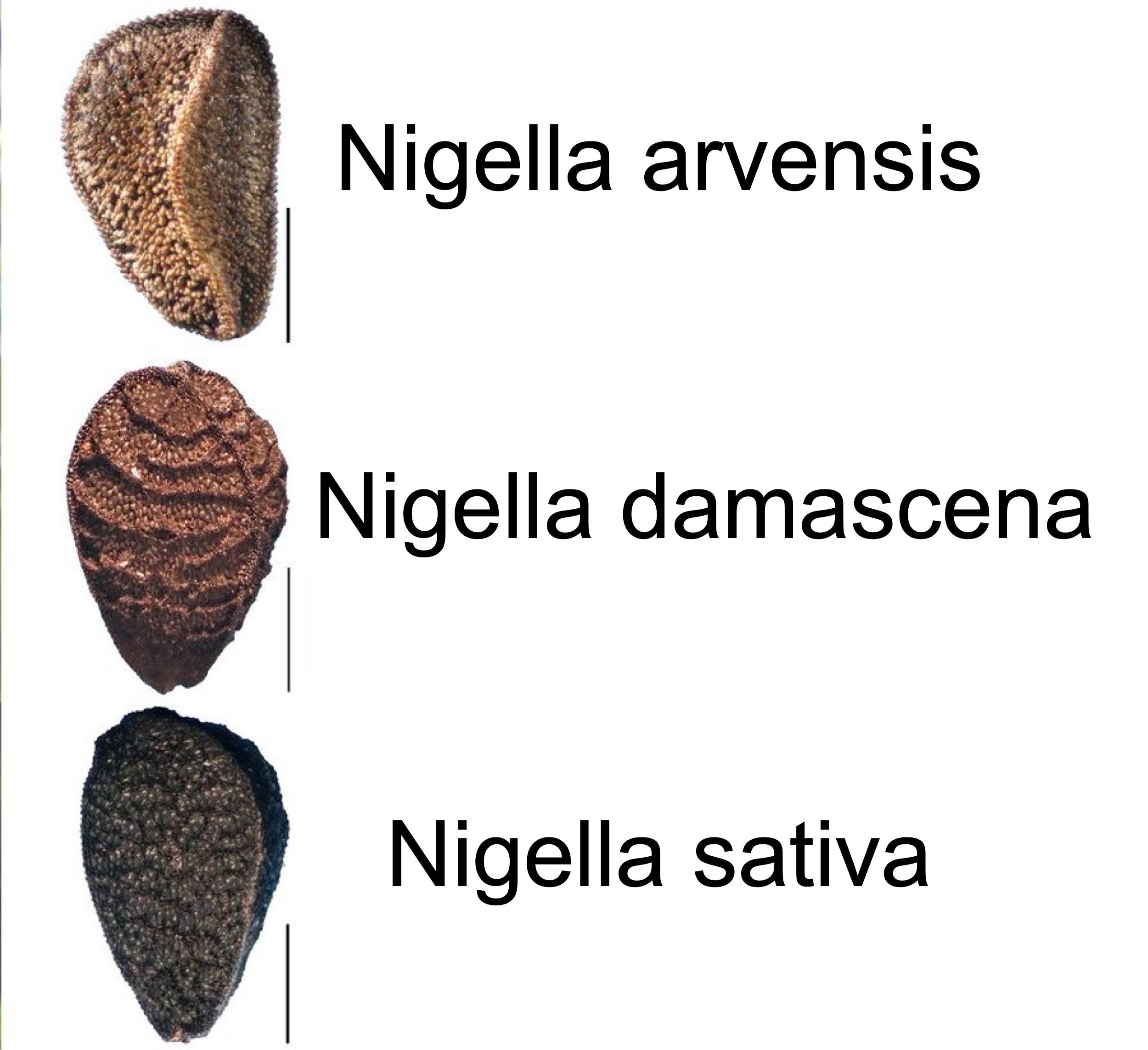
Nigella spp seeds, archeological record by their seeds. Scale bar 1mm.
Nigella prefer light well-drained warm soil, cannot grow in the shade, preferring a sunny position and prefers dry or moist soil.
Easily grown in any good garden soil.
The seeds have a strong aroma and spicy taste, they can be used as a condiment or spice to flavour cakes, breads and curries.
N. sativa grows to 20–30 cm tall, with finely divided leaves. Its flowers pale blue and white, with five to ten petals.
N. damascena grows to 20–50 cm, with pinnately divided, thread-like, alternate leaves. It’s flowers have different shades of blue, can be white, pink, or pale purple, with 5 to 25 sepals. The petals are located at the base of the stamens and are minute and clawed. The sepals are the only colored part of the perianth. The four to five carpels of the compound pistil have each an erect style.
N. arvensis grow up to 30 cm.
The seeds have been reported to have 21% protein, 35.5% fat, 5.5% moisture and 3.7% ash and the rest being total carbohydrate. Nigella sativa water extraction yield is 6.97% w/w or 23.85% v/v.
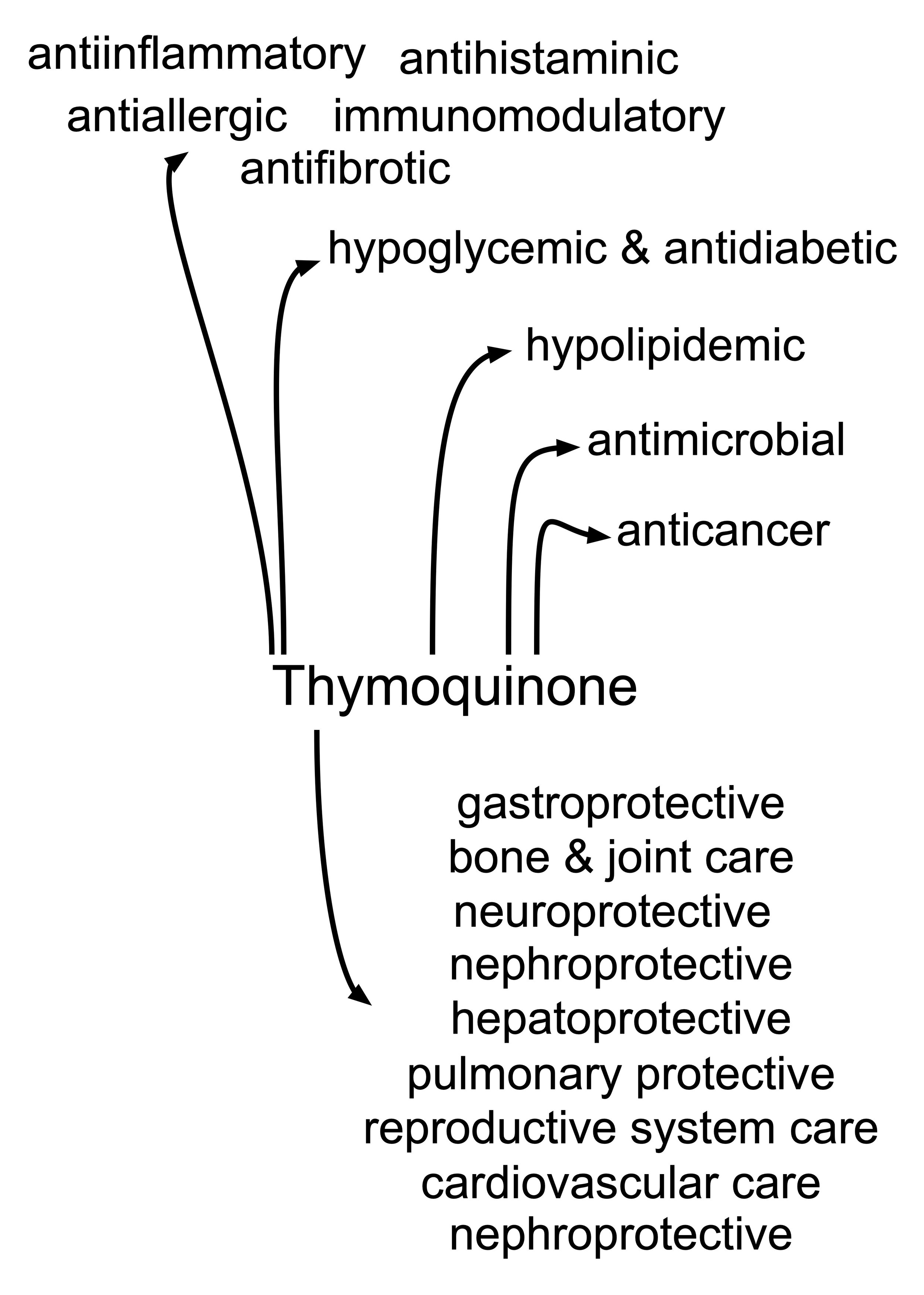
Nigella sativa has several therapeutic effects which are attributed to its constituents like nigellicine, nigellidine, thymoquinone, dithymoquinone, thymol and carvacrol.
Possibly Effective for
Asthma. Research shows that taking black seed by mouth along with asthma medicines can improve coughing, wheezing, and lung function in some people with asthma. But it seems to work only in people with very low lung function before treatment. And it does not seem to work as well as the drugs theophylline or salbutamol.
Thymoquinone has anti-inflammatory properties that prevent the biosynthesis of inflammatory mediators of asthma such as 5-Lipoxygenase, Cyclooxygenase , Prostaglandin D2 and Leukotrienes. Thymoquinone also reduce Lipopolysaccharides-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukins and Tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α). In addition, thymoquinone showed immunomodulatory role in the cellular and humoral immunity.Diabetes. Early research shows that taking black seed powder can improve blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. Black seed might also improve levels of cholesterol in people with diabetes. Doses of 2 grams daily seem to be needed for any benefit.
High blood pressure. Research shows that taking black seed by mouth might reduce blood pressure by a small amount.
To improve sperm function. Research shows that taking black seed oil increases the number of sperm and how quickly they move in men with infertility.
Breast pain (mastalgia). Research shows that applying a gel containing black seed oil to the breasts during the menstrual cycle reduces pain in women with breast pain.
Insufficient Evidence for
A type of leukemia (acute lymphoblastic leukemia). Taking black seed while being treated for this type of cancer might increase the chances of staying cancer-free once treatment ends. But it doesn’t improve overall survival.
Hay fever (allergic rhinitis). Early research suggests that taking black seed oil by mouth daily might improve allergy symptoms in people with hay fever.
Itchy and inflamed skin (eczema). Early research suggests that taking black seed oil by mouth might improve symptoms in people with itchy and inflamed skin. But applying black seed oil ointment to the skin does not seem to help.
A disease that attacks the thyroid (autoimmune thyroiditis). . Taking black seed might improve some but not all measures of thyroid function in people with a disease called Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Dry nose. Early research shows that using a nasal spray containing black seed oil can reduce dryness, blockage, and crusting of the nostrils in elderly patients with nasal irritation.
Indigestion. Taking a product containing black seed oil, honey, and water seems to reduce symptoms of indigestion. It’s unclear if this improvement is due to black seed or other ingredients.
Seizures (epilepsy). Early research shows that taking black seed extract by mouth reduces the number of seizures in children with epilepsy. But taking black seed oil does not seem to work.
Enhance memory and learning in health and illness. Possess mnemonic/nootropic properties. In elderly humans, 500 mg for 9 weeks was also shown to enhance the executive functions in various memory related tests such as logical memory, digit span, letter cancellation, Rey-Osterrieth complex figure, trail making, and stroop tests, with neuro-protective and cholinergic role.
Stomach ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori (H pylori infectoin). Some research shows that taking black seed powder along with the drug omeprazole might help eliminate a certain bacteria (H. pylori) in the stomach that can cause stomach ulcers. But not all doses seem to work.
Hepatitis C. Some research shows that taking black seed powder along with the drug omeprazole might help eliminate a certain bacteria (H. pylori) in the stomach that can cause stomach ulcers. But not all doses seem to work.
High cholesterol. Some early research shows that taking crushed black seed increases "good" high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and reduces total cholesterol, "bad" low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and blood fats called triglycerides in people with borderline high cholesterol. Other research shows that taking both crushed black seed and garlic oil in addition to other products that lower cholesterol, such as simvastatin, can lead to larger improvements in blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels than simvastatin alone. However, not all research agrees.
Metabolic syndrome. Early research suggests that taking a specific black seed oil product twice daily for 6 weeks might reduce total cholesterol, "bad" low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and blood sugar levels in people with metabolic syndrome.
Methotrexate toxicity. Early research shows that taking black seed might reduce liver damage caused by a certain drug used to treat cancer in children with a type of leukemia.
Relieving symptoms related to opioid withdrawal. Early research shows that taking black seed extract by mouth three times daily for 12 days might reduce symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
Osteoarthritis. Early research shows that applying black seed oil to the knee for 3 weeks can help relieve knee pain caused by osteoarthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis. Early research shows that taking black seed oil improves pain and stiffness in people with rheumatoid arthritis who are already taking methotrexate.
Sore throat and swollen tonsils (tonsillopharyngitis). Early research suggests that taking a combination of chanca piedra and black seed by mouth for 7 days relieves pain in people with sore throat and swollen tonsils.
Birth control.
Boosting the immune system.
Bronchitis.
Cancer prevention.
Congestion.
Cough.
Digestive problems including intestinal gas and diarrhea.
Flu.
Headache.
Increasing breast-milk flow.
Menstrual disorders.
Dosing
The following doses have been studied in scientific research:
BY MOUTH:For asthma: 2 grams of ground black seed has been used daily for 12 weeks. Also, 500 mg of black seed oil has been taken twice daily for 4 weeks. In addition, 15 mL/kg of black seed extract has been used daily for 3 months. A single dose of 50-100 mg/kg has also been used.
For diabetes: 1 gram of black seed powder has been used twice daily for up to 12 months.
For high blood pressure: 0.5-2 grams of black seed powder has been taken daily for up to 12 weeks. Also, 100-200 mg of black seed oil has been used twice daily for 8 weeks.
To improve sperm function: 2.5 mL of black seed oil has been used twice daily for 2 months.
ON THE SKIN:
For breast pain: A gel containing 30% black seed oil has been applied to breasts every day for two menstrual cycles.
Nigella sativa and thymoquinone have the protective effects against neurodegenerative diseases, including; Alzheimer, depression, encephalomyelitis, epilepsy, ischemia, Parkinson, and traumatic brain injury have been discussed in the cell lines and experimental animal models.
In a case study, Nigella sativa extract turns an HIV patient to be seronegative in 6 months.
Thymoquinone a monoterpene diketone, forms 18.4%–24% of Nigella sativa essential oils (1-1.2%) with a boiling point and melting point of 230–232°C and 44‐45°C, respectively.It’s probably the most useful known component of Nigella sativa.
Its molecular weight is 164.204 g/mol, and value of Log is 2.20 denoting lipophilicity of thymoquinone.It has the ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) owing to its molecular weight (less than 500 g/mol) and Log (less than five) value.TQ converted to DTQ via photodimerization, as a consequence of exposure to heat and sunlight, so stored at 4Cº away from direct sun light. TQ is unstable in aqueous solutions, particularly at an alkaline pH, so aqueous solutions are inappropriate as pharmaceutical vehicles for TQ preparations.
The solubility of thymoquinone in ethanol and DMF is approximately 16 mg/ml and in DMSO it is approximately 14 mg/ml. Thymoquinone is sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers and water solubility is >500 μg/mL.
Liver enzymes, such as DT-diaphorase (a quinine reductase), catalyzes the reduction of TQ into a dihydrothymoquinone which antioxidant properties are more potent than those of thymoquinone and similar to those of Trolox, which considers a standard antioxidant compound.
The oral and intra-peritoneal (i.p.) median lethal doses (LD50) for TQ in rats as well as in mice were successfully determined by several research groups.
At higher doses, it is well tolerated by male and female rats. Thymoquinone at 10 mg/kg body weight was found to have no observed adverse effect level. Moreover, the administration of 20 ml develops a thymoquinone-rich fraction nanoemulsion per kg that was not toxic following acute exposure in Sprague-Dawley rats.
In terms of acute toxicity, thymoquinone-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (TQ-NLC) have less toxicity than pure thymoquinone. In a subacute toxicity study, oral administration of 100 mg/kg of TQ-NLC caused mortality in neither male nor female mice but resulted in liver toxicity. For long-term oral consumption, thymoquinone and TQ-NLC at doses of 10 mg/kg are safe in mice.
Furthermore, another study determined LD50 = 104.7 mg/kg in mice i.p. and 870.9 mg/kg after oral ingestion of thymoquinone. In rats, the value of LD50 was detected to be 57.5 mg/kg while it was 794.3 mg/kg after i.p. and oral administration, respectively. Interestingly, using thymoquinone in combination with ionizing radiation such as γ-radiation was found to exert a synergistic cytotoxic effect on breast cancer cells in vitro.
Thymoquinone medical significance is more in nervous system disorders. Nigella sativa can improve memory impairment, learning, anxiety, depression, epilepsy, neurotoxicity, neurodegeneration and pain.
Thymoquinone is slowly absorbed after oral administration, absolute bioavailability is around 50%, with elimination half life of about 5 hours, and considerable water solubility (> 500 μg/mL), which may be enough to exert pharmacologic effects after parenteral route administration.
Thymoquinone recovery is 0.4–0.5% in hydrodistillation (yield of 1.0–1.2% of essential oil with 30–32% of thymoquinone) , 1.85% in SFE of 28 MPa at 50°C (yield of 26.02% with 7.11% of thymoquinone) and 0.95% in SFE of 12 MPa at 40°C (yield of 7.8% with thymoquinone content of 12.27%) at a CO2 mass flow rate of 3.3–8.05 × 10−4 kg/s.
Nigella sativa fat has anti-fatigue effect by increasing time to exhaust threshold in training by 18% (0.27g/kg/day, 21 days).
Antidepressant effect is obvious in doses of 30-60 mg/kg/day of Nigella sativa extract. Thymoquinone is one of the active phytochemicals.
Thymoquinone at 0.8-1.0 mg/kg/day, has prophylactic anti-anxiety effects ;and at 1.6-1.8 mg/kg/day, has anxiolytic effect.
Nigella sativa oil has a potential neuroprotective function against neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disorders like Parkisnon’s disease ,Alzheimer’s disease, amyloidosis, and multiple sclerosis at doses of 1.5-2.25 mg/kg/day. Thymoquinone in the right dose is 90% protective and 50% curative for oxidative stress mediated autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Nigella sativa 6mg/kg/day over two months can restore considerable part of aged people olfactory function.
Nigella sativa at doses of 55 mg/kg (or 7 mg/kg of thymoquinone) once a day orally for 4-12 weeks, protects against acute traumatic nervous stress like sciatica and in stroke. 1mg/kg/day of thymoquinone may improve prognosis of patients susceptible to cerebral or cerebellar stroke.
Thymoquinone doses of 1mg/kg/day over 14 days improves pain threshold, or 7-60 mg/kg/day of Nigella sativa fat.
Actually, all forms of Nigella sativa extracts, as well as fat and thymoquinone can relieve pain.
Nigella sativa is effective in long-term treatment of opioid dependence, 500 mg a day reduce opiate withdrawal signs score to the third in less than 2 weeks.
Nigella sativa and its extract can be useful in the treatment of drug tolerance.
Nigella sativa improve memory, cognition and attentiveness in elderly individuals. 30-60 mg/kg/day of Nigella sativa may restore memory to some extent in 2-3 weeks, and improve learning.
Nigella sativa extract should be taken with precaution in cases of motor coordination disorders like ataxia and locomotor disorders.
Nigella sativa fat has anti epileptic effect at doses of 0.6m/kg for 21+ days. Few studies showed as well its beneficial effect on childhood epilepsy.
Thymoquinone (injected 1mg/kg/day) has nearly 90% preventive and 50% therapeutic effects in chronic relapsing autoimmune encephalitis in female Lewis rats.
Thymoquinone, particularly at a concentration of 0.4%, may be considered for topical application alone in the treatment of acute otitis externa, without any requirement for a combined treatment.
Thymoquinone was shown to have an inhibitory effect, comparable with that of triamcinolone, on corneal neovascularization in rat model. It decreased corneal neovascularization in a dose-dependent manner, and a 0.4% concentration effect was comparable to that of triamcinolone acetonide.
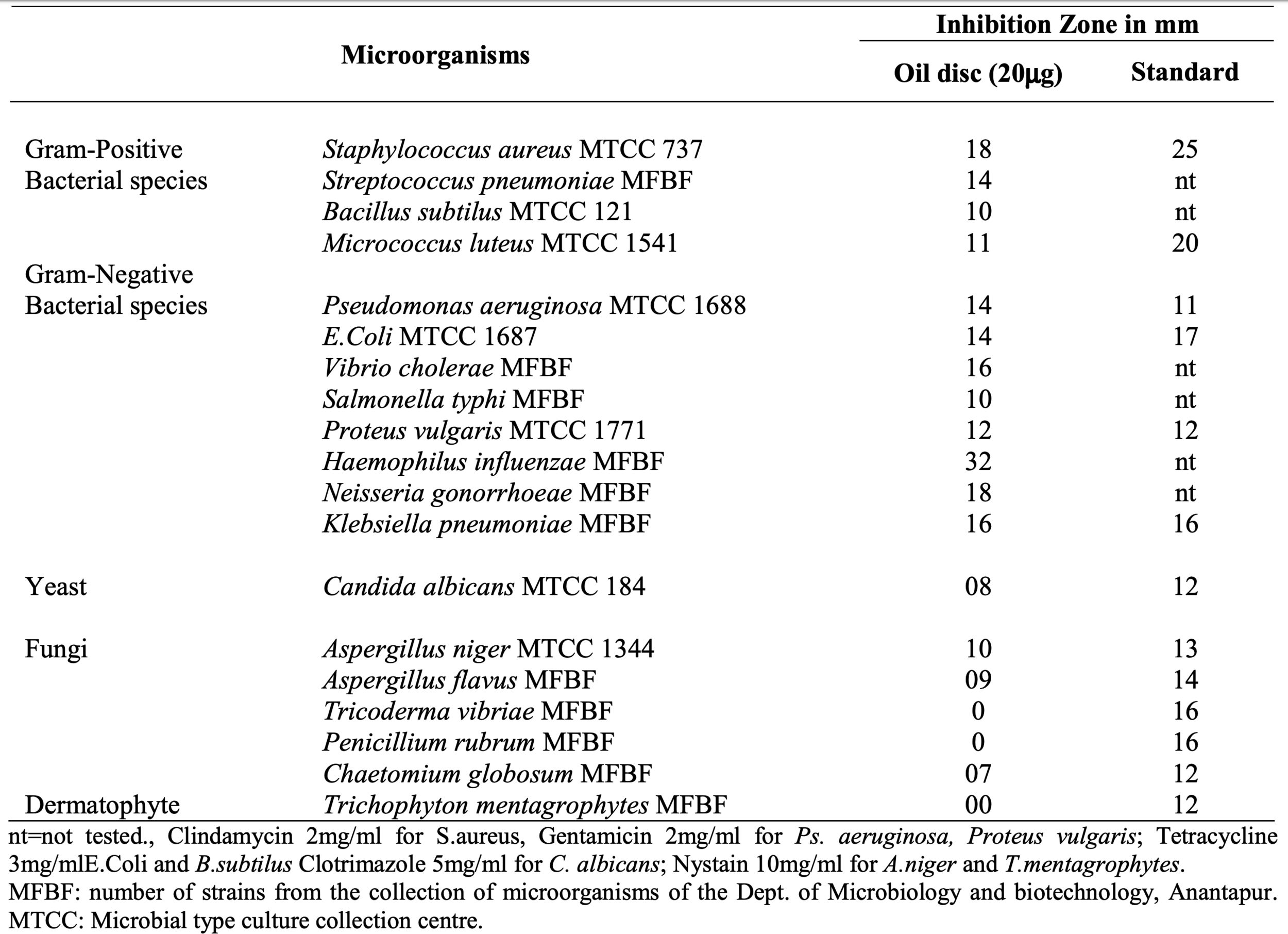
Thymoquinone has bactericidal activity with MICs values ranged from 8 to 32 μg/ml, especially Gram positive cocci types such as Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. For Staphylococcus aureus, clear inhibition of the growth was found by concentration of 300 mg/ml.
Thymoquinone antifungal IC50 values was 2.308 µg/ml for Candida parapsilosis (Amphotericin B. IC50 57.68 µg/ml) and 9.313 µg/ml for Cryptococcus laurentii (Amphotericin B. IC50 15.50 µg/ml). It is also found that thymoquinone has an antifungal activity with IC50 against Cryptococcus albidus which is 20.83 µg/ml, Candida albicans 23.33 µg/ml, Issatchenkia orientalis 25.33 µg/ml, and Aspergillus fumigatus23.40 µg/ml.
Intracrevicular application of 0.2% Thymoquinone gel could be a beneficial adjunct to scaling and root planing in treating chronic periodontitis.
Thymoquinone increase acetylcholinesterase activity in rat plasma with decreased acetylcholine activity.
Thymoquinone anticancer activity
Nigella sativa fat (commonly referred to as oil) is fatty acids extracted by cold press of Nigella sativa seeds. Once cleared from the smashed black ash suspension of seeds capsule, it shows a clear yellow-greenish color.
Nigella sativa fat is rich in:
Unsaturated fats; mainly linoleic acid (50-60%), oleic acid (20%), eicodadienoic acid (3%) and dihomolinoleic acid (10%).
Saturated fats; including palmitic, stearic acid up to 30%.
Other compounds; esters of unsaturated fatty acids with C15 and higher terpenoids, esters of dehydrostearic and linoleic acid, aliphatic alcohol and β-unsaturated hydroxy ketone. α-sitosterol is a major sterol, which represents 44-54% of the aggregate sterols, followed by stigmasterol that is 6.57-20.92% of total sterols.
Examples of other reported chemical components includes nigellone, avenasterol-5-ene, avenasterol7-ene, campesterol, cholesterol, citrostadienol, cycloeucalenol, gramisterol, lophenol, obtusifoliol, stigmastanol, stigmasterol-7-ene, β-amyrin, butyrospermol, cycloartenol, 24-methylene-cycloartanol, taraxerol, tirucallol, 3-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl (1.3)-α L-rhamnopyranosyl(1.2)-β-L-arabino-pyranosyl]-28-O-[ β-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1.4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1.6)-β-Dgluco- pyranosyl] hederagenin, hederagenin glycoside, melanthin, melanthigenin, bitterprinciple, tannin, resin, protein, reducing sugar, glycosidalsaponin, 3-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl (1.2)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1.2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]-11-methoxy-16, 23 dihydroxy-28-methy-lolean-12-enoate,stigma-5, 22-dien3-β-D-gluco-pyranoside, cycloart-23-methyl-7, 20, 22triene- 3., 25-diol, nigellidine-4-O-sulfite, N. mines A3,A4, A5, C, N. mines A1, A2, B1, and B2.
Nigella sativa fixed oil fatty acids composition:
Lauric acid 0.6 %
Myristic acid 0.5 %
Palmitic acid 12.5 %
Stearic acid 1.5 - 3.4 %
Oleic acid 20.4 - 23.4 %
Linoleic acid 55.6 - 59.8 %
Linolenic acid 0.4 %
Eicosadienoic acid 3.1 %
Nigella sativa fat
Nigella sativa essential oil
Major Nigella sativa essential oil composition:
Monoterpene hydrocarbons (51.2-60.2%)
Ketones (46.1-59.9 %)
Thymoquinone 42.3 - 56.1 %
P-cymene 23.1 - 31.5 %
Dehydro-sabina ketone 3.1 - 3.3 %
Carvacrol 1.3 - 1.4 %
Longifolene 1.5 - 2.1 %
Nigella sativa essential oil in the other hand is obtained by distillation. Its red, volatile and much lighter than the fat, and rich in thymoquinone (43-56%).
TQ (30%-48%), thymohydroquinone, dithymoquinone, p-cymene (7%-15%), carvacrol (6%-12%), 4-terpineol (2%-7%), t-anethol (1%-4%), sesquiterpenelongifolene (1%-8%), α-pinene and thymol and so forth.
The seeds also contain two separate sorts of alkaloids i.e. isoquinoline alkaloids e.g. nigellicimine and nigellicimine N-oxide, and pyrazol alkaloids or indazole ring bearing alkaloids which incorporate nigellidine and nigellicine
Nigella sativa seeds additionally contain alpha-hederin, a water soluble pentacyclic triterpene and saponin, a potential anticancer agent.
Nigella sativa seeds are rich in healthy fat (28.5%), protein (27%), carbohydrates (25%), crude fiber (8.5%) with total ash less than 5%, with various vitamins and minerals like Zn, Fe, P, and Cu.
The seeds contain carotene which is transformed by the liver to vitamin A. Root and shoot of the plant are reported to contain vanillic acid
Nigella sativa fat is rich in:
Unsaturated fats; mainly linoleic acid (50-60%), oleic acid (20%), eicodadienoic acid (3%) and dihomolinoleic acid (10%).
Saturated fats; including palmitic, stearic acid up to 30%.
Other compounds; esters of unsaturated fatty acids with C15 and higher terpenoids, esters of dehydrostearic and linoleic acid, aliphatic alcohol and β-unsaturated hydroxy ketone. α-sitosterol is a major sterol, which represents 44-54% of the aggregate sterols, followed by stigmasterol that is 6.57-20.92% of total sterols.
Examples of other reported chemical components includes nigellone, avenasterol-5-ene, avenasterol7-ene, campesterol, cholesterol, citrostadienol, cycloeucalenol, gramisterol, lophenol, obtusifoliol, stigmastanol, stigmasterol-7-ene, β-amyrin, butyrospermol, cycloartenol, 24-methylene-cycloartanol, taraxerol, tirucallol, 3-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl (1.3)-α L-rhamnopyranosyl(1.2)-β-L-arabino-pyranosyl]-28-O-[ β-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1.4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1.6)-β-Dgluco- pyranosyl] hederagenin, hederagenin glycoside, melanthin, melanthigenin, bitterprinciple, tannin, resin, protein, reducing sugar, glycosidalsaponin, 3-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl (1.2)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1.2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]-11-methoxy-16, 23 dihydroxy-28-methy-lolean-12-enoate,stigma-5, 22-dien3-β-D-gluco-pyranoside, cycloart-23-methyl-7, 20, 22triene- 3., 25-diol, nigellidine-4-O-sulfite, N. mines A3,A4, A5, C, N. mines A1, A2, B1, and B2.
Nigella sativa essential oil antimicrobial activity